Page 432 - IJB-9-4
P. 432
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting of artificial blood vessel
thousands of droplets in seconds through printing in a
. The inkjet bioprinting methods
Medium level are characterized by microdropletization as well as
non-contact manner
[185]
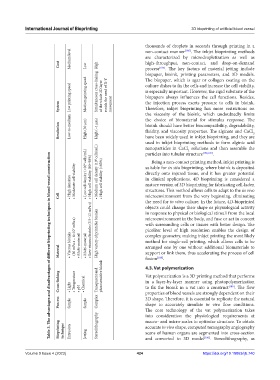
Cost Low High high-throughput, non-contact, and drop-on-demand
. The key factors of material jetting include
process
[185]
biopaper, bioink, printing parameters, and 3D models.
The biopaper, which is agar or collagen coating on the
Low printing speed Medium printing speed Simultaneous cross-linking of the whole 2D layer avoids the need of X-Y culture dishes to fix the cells and increase the cell viability,
is especially important. However, the rigid substrate of the
biopapers always influences the cell functions. Besides,
the injection process exerts pressure to cells in bioink.
System movement Therefore, inkjet bioprinting has more restrictions on
the viscosity of the bioink, which undoubtedly limits
Resolution Low-to-medium High (30 μm) High (~1 μm) the choice of biomaterial for stimulus response. The
bioink should have better biocompatibility, degradability,
fluidity, and viscosity properties. The alginate and CaCl
2
have been widely used in inkjet bioprinting, and they are
used in inkjet bioprinting methods to form alginic acid
nanoparticles in CaCl solutions and then assemble the
2
.
particles into tubular structure
[186,187]
Table 3. The advantages and disadvantages of different bioprinting techniques in blood vessel construction
Being a non-contact printing method, inkjet printing is
directly onto injured tissue, and it has greater potential
• High densities • Moderate cell viability • Low cell density (<10 6 cells/mL) • High cell viability (80–90%) • Medium cell density (10 8 cells/mL) • High cell viability (>85%) suitable for in situ bioprinting, where bioink is deposited
in clinical applications. 4D bioprinting is considered a
mature version of 3D bioprinting for fabricating cell-laden
structures. This method allows cells to adapt to the in vivo
Cell microenvironment from the very beginning, eliminating
the need for in vitro culture. In the future, 4D-bioprinted
objects could change their shape or physiological activity
in response to physical or biological stimuli from the local
microenvironment in the body, and fuse or act in concert
picoliter level of high resolution enables the design of
• Viscous bioinks (30 mPa·s – 6×10 7 mPa·s) • Multi‑material • Multi‑material • Low viscous bioinks (3.5–12 mPa·s) High variety of printable bioinks with surrounding cells or tissues with better design. The
complex geometry, making inkjet printing the most likely
method for single-cell printing, which allows cells to be
arranged one by one without additional biomaterials to
Material support or link them, thus accelerating the process of cell
fusion
.
[188]
Cross‑linking • Light • Temperature • pH • Chemical Transparent and photosensitive bioink 4.3. Vat polymerization [189] . The flow
Vat polymerization is a 3D printing method that performs
in a layer-by-layer manner using photopolymerization
to fix the bioink in a vat into a construct
3D shape. Therefore, it is essential to replicate the natural
Process Simple Simple Complex properties of blood vessels are strongly dependent on their
shape to accurately simulate in vivo flow conditions.
The core technology of the vat polymerization takes
into consideration the physiological requirements at
Bioprinting technique Extrusion Jetting Stereolithography macro- and micro-scales to optimize structure. To obtain
accurate in vivo shape, computed tomography angiography
scans of human organs are segmented into cross-section
and converted to 3D model
. Stereolithography, as
[190]
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 424 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.740