Page 431 - IJB-9-4
P. 431
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting of artificial blood vessel
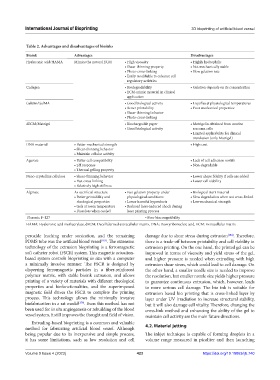
Table 2. Advantages and disadvantages of bioinks
Bioink Advantages Disadvantages
Hyaluronic acid/HAMA Mimics the natural ECM • High viscosity • Highly hydrophilic
• Shear‑thinning property • Not mechanically stable
• Photo‑cross‑linking • Slow gelation rate
• Easily modifiable to enhance cell
regulatory activities
Collagen • Biodegradability • Gelation depends on its concentration
• ECM‑mimic material in clinical
application
Gelatin/GelMA • Good biological activity • Liquifies at physiological temperatures
• Better printability • Poor mechanical properties
• Shear‑thinning behavior
• Photo‑cross‑linking
dECM/Matrigel • Biochargeable paper • Matrigel is obtained from murine
• Good biological activity sarcoma cells
• Limited applicability for clinical
translation (only Matrigel)
DNA material • Better mechanical strength • High cost
• Shear‑thinning behavior
• Maintain cellular activity
Agarose • Better cell compatibility • Lack of cell adhesion motifs
• pH response • Non‑degradable
• Thermal gelling property
Nano-crystalline cellulose • Shear‑thinning behavior • Lower shape fidelity if cells are added
• Fast cross‑linking • Lower cell viability
• Relatively high stiffness
Alginate As sacrificial structure • Fast gelation property under • Biological inert material
• Better printability and physiological conditions • Slow degradation when not cross‑linked
rheological properties • Lesser harmful byproducts • Low mechanical strength
• Gels at room temperature • Reduced laser‑induced shock during
• Dissolves when cooled laser printing process
Pluronic F‑127 • Poor biocompatibility
HAMA: Hyaluronic acid methacrylate, dECM: Decellularized extracellular matrix, DNA: Deoxyribonucleic acid, ECM: Extracellular matrix
peroxide leaching under sonication, and the remaining damage due to shear stress during extrusion [184] . Therefore,
PDMS tube was the artificial blood vessel [183] . The extension there is a trade-off between printability and cell viability in
technology of the extrusion bioprinting is a ferromagnetic extrusion printing. On the one hand, the printed gel can be
soft catheter robot (FSCR) system. This magnetic actuation- improved in terms of viscosity and yield stress of the gel,
based system controls bioprinting in situ with a computer and higher pressure is needed when extruding with high
a minimally invasive manner. The FSCR is designed by extrusion shear stress, which could lead to cell damage. On
dispersing ferromagnetic particles in a fiber-reinforced the other hand, a smaller needle size is needed to improve
polymer matrix, with stable bioink extrusion, and allows the resolution, but smaller nozzle size yields higher pressure
printing of a variety of materials with different rheological to guarantee continuous extrusion, which, however, leads
properties and biofunctionalities, and the superimposed to more serious cell damage. The bio ink is suitable for
magnetic field drives the FSCR to complete the printing extrusion based bio printing that is cross-linked layer by
process. This technology allows the minimally invasive layer under UV irradiation to increase structural stability,
biofabrication in a rat model [179] . Even this method has not but it will also damage cell vitality. Therefore, changing the
been used for in situ angiogenesis or rebuilding of the blood cross-link method and enhancing the ability of the gel to
vessel system, it still improves the thought and field of vision. maintain cell activity are the main future directions.
Extruding-based bioprinting is a common and valuable
method for fabricating artificial blood vessel. Although 4.2. Material jetting
being popular due to its inexpensive and simple process, The inkjet technique is capable of forming droplets in a
it has some limitations, such as low resolution and cell volume range measured in picoliter and then launching
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 423 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.740