Page 426 - IJB-9-4
P. 426
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D bioprinting of artificial blood vessel
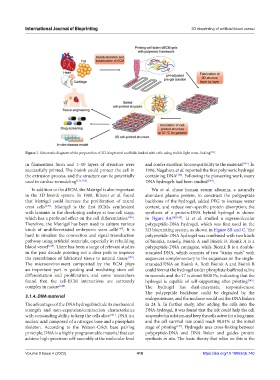
Figure 7. Schematic diagram of the preparation of 3D-bioprinted scaffolds loaded with cells using visible light cross-linking [134] .
in filamentous form and 1–10 layers of structure were and confer excellent biocompatibility to the material [142] . In
successfully printed. The bioink could protect the cell in 1996, Nagahara et al. reported the first polymeric hydrogel
the extrusion process, and the structure can be potentially containing DNA [143] . Following the pioneering work, many
used in cardiac remodeling [131,134] . DNA hydrogels had been studied [144] .
In addition to the dECM, the Matrigel is also important Wu et al. chose human serum albumin, a naturally
in the 3D bioink system. In 1988, Bilozur et al. found abundant plasma protein, to construct the polypeptide
that Matrigel could increase the proliferation of neural backbone of the hydrogel, added PEG to increase water
crest cells [135] . Matrigel is the first ECMs synthesized content, and reduce non-specific protein absorption; the
with laminin in the developing embryo at two-cell stage, synthesis of a protein-DNA hybrid hydrogel is shown
which has a profound effect on the cell differentiation [136] . in Figure 8A [142,145] . Li et al. studied a supramolecular
Therefore, the Matrigel has been used to culture various polypeptide-DNA hydrogel, which was first used in the
kinds of undifferentiated embryonic stem cells [137] . It is 3D bioprinting system, as shown in Figure 8B and C. The
hard to simulate the connection and signal transduction polypeptide-DNA hydrogel was combined with two kinds
pathway using artificial materials, especially in rebuilding of bioinks, namely, Bioink A and Bioink B. Bioink A is a
blood vessel [138] . There has been a surge of relevant studies polypeptide-DNA conjugate, while Bioink B is a double-
in the past decade pointing out a clear path to improve stranded DNA, which consists of two “sticky ends” with
the resemblance of fabricated tissue to natural tissue [139] . sequences complementary to the sequences on the single-
The microenvironment composited by the ECM plays stranded DNA on Bioink A. Both Bioink A and Bioink B
an important part in guiding and mediating stem cell could format the hydrogel under phosphate-buffered saline
differentiation and proliferation, and some researchers in seconds and the G’ is about 5000 Pa, indicating that the
found that the cell-ECM interactions are extremely hydrogel is capable of self-supporting after printing [146] .
complex in nature [140] . The hydrogel has dual-enzymatic responsiveness:
The polypeptide backbone could be degraded by the
3.1.4. DNA material endoproteinase, and the nuclease would cut the DNA linkers
The advantages of the DNA hydrogel include its mechanical in 24 h. In further study, after adding the cells into the
strength and non-expansion/contraction characteristics DNA-hydrogel, it was found that the ink could help the cell
with outstanding ability to keep the cells alive [141] . DNA is a suspended in solution and keep the cells active for a long time,
nucleic acid composed of a nitrogen base and a phosphate and the cell survival rate could reach 98.81% at the initial
skeleton. According to the Watson-Crick base pairing stage of printing [147] . Hydrogels uses cross-linking between
principle, DNA is a highly programmable material that can polypeptide-DNA and DNA linker and guides protein
achieve high-precision self-assembly at the molecular level synthesis in situ. The basic theory that relies on this is the
Volume 9 Issue 4 (2023) 418 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.740