Page 397 - IJB-9-5
P. 397
International Journal of Bioprinting A sturgeon cartilage extracellular matrix-derived bioactive bioink
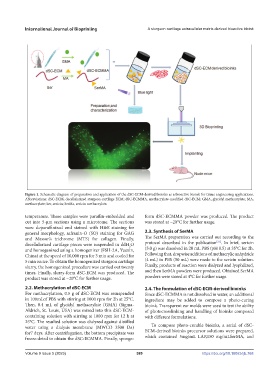
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of preparation and application of the dSC-ECM-derived bioinks as a bioactive bioink for tissue engineering applications.
Abbreviations: dSC-ECM, decellularized sturgeon cartilage ECM; dSC-ECMMA, methacrylate-modified dSC-ECM; GMA, glycidyl methacrylate; MA,
methacrylate; Ser, sericin; SerMa, sericin methacrylate.
temperature. These samples were paraffin-embedded and form dSC-ECMMA powder was produced. The product
cut into 5-μm sections using a microtome. The sections was stored at −20°C for further usage.
were deparaffinized and stained with H&E staining for
general morphology, safranin-O (SO) staining for GAG 2.3. Synthesis of SerMA
and Masson’s trichrome (MTS) for collagen. Finally, The SerMA preparation was carried out according to the
[21]
decellularized cartilage pieces were suspended in ddH O protocol described in the publication . In brief, sericin
2
and homogenized using a homogenizer (FSH‐2A, Yuexin, (5.0 g) was dissolved in 20 mL PBS (pH 8.5) at 35°C for 2h.
China) at the speed of 10,000 rpm for 3 min and cooled for Following that, dropwise additions of methacrylic anhydride
5 min on ice. To obtain the homogenized sturgeon cartilage (4 mL) in PBS (50 mL) were made to the sericin solution.
slurry, the homogenized procedure was carried out twenty Finally, products of reaction were dialyzed and lyophilized,
times. Finally, slurry-form dSC-ECM was produced. The and then SerMA powders were produced. Obtained SerMA
product was stored at −20°C for further usage. powders were stored at 4°C for further usage.
2.2. Methacrylation of dSC-ECM 2.4. The formulation of dSC-ECM-derived bioinks
For methacrylation, 0.5 g of dSC-ECM was resuspended Since dSC-ECMMA is not dissolved in water, an additional
in 100mLof PBS with stirring at 1000 rpm for 2h at 25°C. ingredient may be added to compose a photo-curing
Then, 0.4 mL of glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) (Sigma- bioink. Transparent ear molds were used to test the ability
Aldrich, St. Louis, USA) was mixed into this dSC-ECM- of photocrosslinking and handling of bioinks composed
containing solution with stirring at 1000 rpm for 12 h at with different formulations.
25°C. The resulted solution was dialyzed against distilled
water using a dialysis membrane (MWCO 3500 Da) To compose photo-curable bioinks, a serial of dSC-
for7 days. After centrifugation, the bottom precipitate was ECM-derived bioinks precursor solutions were prepared,
freeze-dried to obtain the dSC-ECMMA. Finally, sponge- which contained 5mg/mL LAP,150 mg/mLSerMA, and
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 389 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.768