Page 71 - IJB-9-5
P. 71
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed PLA-BG composite induces angiogenesis
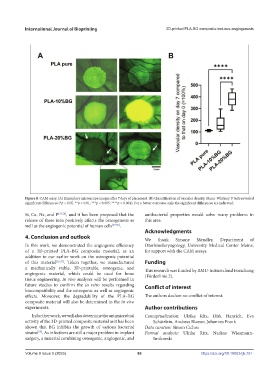
Figure 8. CAM assay. (A) Exemplary microscope images after 7 days of placement. (B) Quantification of vascular density. Mann-Whitney U tests revealed
significant differences (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005; ****p < 0.001). For a better overview, only the significant differences are indicated.
Si, Ca, Na, and P [17,58] , and it has been proposed that the antibacterial properties would solve many problems in
release of these ions positively affects the osteogenesis as this area.
well as the angiogenic potential of human cells [47,58] .
Acknowledgments
4. Conclusion and outlook We thank Simone Mendler, Department of
In this work, we demonstrated the angiogenic efficiency Otorhinolaryngology, University Medical Center Mainz,
of a 3D-printed PLA–BG composite material, as an for support with the CAM assays.
addition to our earlier work on the osteogenic potential
of this material [16,17] . Taken together, we manufactured Funding
a mechanically stable, 3D-printable, osteogenic, and This research was funded by RMU-Initiativfond Forschung
angiogenic material, which could be used for bone (Förderlinie 2).
tissue engineering. In vivo analyses will be performed in
future studies to confirm the in vitro results regarding Conflict of interest
biocompatibility and the osteogenic as well as angiogenic
effects. Moreover, the degradability of the PLA–BG The authors declare no conflict of interest.
composite material will also be determined in the in vivo
experiments. Author contributions
In further work, we will also determine the antimicrobial Conceptualization: Ulrike Ritz, Dirk Henrich, Eva
activity of the 3D-printed composite material as it has been Schätzlein, Andreas Blaeser, Johannes Frank
shown that BG inhibits the growth of various bacterial Data curation: Simon Cichos
strains . As infections are still a major problem in implant Formal analysis: Ulrike Ritz, Nadine Wiesmann-
[59]
surgery, a material combining osteogenic, angiogenic, and Imilowski
Volume 9 Issue 5 (2023) 63 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.751