Page 121 - IJB-9-6
P. 121
International Journal of Bioprinting Exosome-based bioink for bioprinting
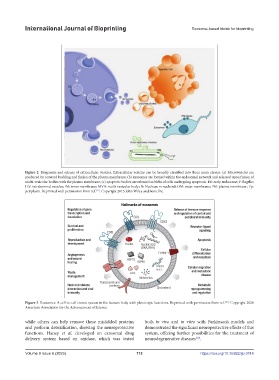
Figure 2. Biogenesis and release of extracellular vesicles. Extracellular vesicles can be broadly classified into three main classes: (a) Microvesicles are
produced by outward budding and fission of the plasma membrane; (b) exosomes are formed within the endosomal network and released upon fusion of
multi-vesicular bodies with the plasma membrane; (c) apoptotic bodies are released as blebs of cells undergoing apoptosis. EE: early endosome; F: flagella;
ILV: intraluminal vesicles; IM: inner membrane; MVB: multi-vesicular body; N: Nucleus; n: nucleoid; OM: outer membrane; PM: plasma membrane ; Pp:
[17]
periplasm. Reprinted with permission from ref. . Copyright 2015 John Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Figure 3. Exosomes: A cell-to-cell transit system in the human body with pleiotropic functions. Reprinted with permission from ref. . Copyright 2020
[18]
American Association for the Advancement of Science.
while others can help remove these misfolded proteins both in vivo and in vitro with Parkinson’s models and
and perform detoxification, showing the neuroprotective demonstrated the significant neuroprotective effects of this
functions. Haney et al. developed an exosomal drug system, offering further possibilities for the treatment of
delivery system based on oxidase, which was tested neurodegenerative diseases .
[30]
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 113 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0114