Page 192 - IJB-9-6
P. 192
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D-printed assembly anatomical patella fracture bone plate
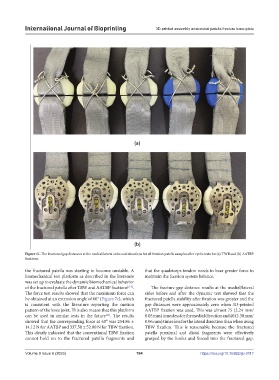
Figure 11. The fractured gap distances at the medial/lateral sides and situations for all fixation patella samples after cyclic tests for (a) TWB and (b) AATBP
fixations.
the fractured patella was starting to become unstable. A that the quadriceps tendon needs to bear greater force to
biomechanical test platform as described in the literature maintain the fixation system balance.
was set up to evaluate the dynamic biomechanical behavior
of the fractured patella after TBW and AATBP fixations [2-5] . The fracture gap distance results at the medial/lateral
The force test results showed that the maximum force can sides before and after the dynamic test showed that the
be obtained at an extension angle of 60° (Figure 7c), which fractured patella stability after fixation was greater and the
is consistent with the literature reporting the motion gap distances were approximately zero when 3D-printed
pattern of the knee joint. This also means that this platform AATBP fixation was used. This was almost 75 (2.24 mm/
can be used in similar tests in the future . The results 0.03 mm) times less for the medial direction and 40 (2.30 mm/
[23]
showed that the corresponding force at 60° was 254.86 ± 0.06 mm) times less for the lateral direction than when using
14.12 N for AATBP and 337.58 ± 52.00 N for TBW fixation. TBW fixation. This is reasonable because the fractured
This clearly indicated that the conventional TBW fixation patella proximal and distal fragments were effectively
cannot hold on to the fractured patella fragments and grasped by the hooks and forced into the fractured gap.
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 184 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0117