Page 203 - IJB-9-6
P. 203
International Journal of Bioprinting Attractiveness of 4D printing in medical field
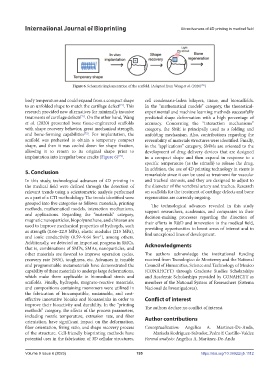
Figure 6. Schematic implementation of the scaffold. (Adapted from Wang et al. (2020) )
[72]
body temperature and could expand from a compact shape cell condensate-laden bilayers, tissue, and bioscaffolds.
to an unfolded shape to match the cartilage defect . This In the “mathematical models” category, the theoretical-
[71]
research provided new alternatives for minimally invasive experimental and machine learning methods successfully
treatments of cartilage defects . On the other hand, Wang predicted shape deformation with a high percentage of
[71]
et al. (2020) presented bone tissue-engineered scaffolds accuracy. Concerning the “interaction mechanisms”
with shape recovery behavior, great mechanical strength, category, the SME is principally used as a folding and
and bone-forming capabilities . For implantation, the unfolding mechanism. Also, contributions regarding the
[72]
scaffold was preheated to obtain a temporary compact reversibility of materials structures were identified. Finally,
shape, and then it was cooled down for shape fixation, in the “applications” category, SMMs are oriented to the
allowing it to return to its original shape prior to development of drug delivery devices that are designed
implantation into irregular bone cracks (Figure 6) . in a compact shape and then expand in response to a
[72]
specific temperature (as the stimuli) to release the drug.
In addition, the use of 4D printing technology in stents is
5. Conclusion remarkable since it can be used as treatment for vascular
In this study, technological advances of 4D printing in and tracheal stenosis, and they are designed to adjust to
the medical field were defined through the detection of the diameter of the vertebral artery and trachea. Research
relevant trends using a scientometric analysis performed on scaffolds for the treatment of cartilage defects and bone
as a part of a CTI methodology. The trends identified were regeneration are currently ongoing.
grouped into five categories as follows: materials, printing The technological advances revealed in this study
methods, mathematical models, interaction mechanisms, support researchers, academics, and companies in their
and applications. Regarding the “materials” category, decision-making processes regarding the direction of
magnetic nanoparticles, biopolyurethane, and chitosan are their efforts in R&D and innovation in the medical field,
used to improve mechanical properties of hydrogels, such providing opportunities to boost areas of interest and to
as strength (0.66–22.9 MPa), elastic modulus (215 MPa), find unexplored lines of development.
and ionic conductivity (8.59–9.64 Sm ), among others.
–1
Additionally, we detected an important progress in SMCs, Acknowledgments
that is, combinations of SMPs, SMAs, nanoparticles, and
other materials are favored to improve operation cycles, The authors acknowledge the institutional funding
recovery rate (98%), toughness, etc. Advances in tunable received from Tecnologico de Monterrey and the National
and programmable metamaterials have demonstrated the Council of Humanities, Science and Technology of Mexico
capability of these materials to undergo large deformations, (CONAHCYT) through Graduate Studies Scholarships
which make them applicable in biomedical stents and and Academic Scholarships provided by CONAHCYT as
scaffolds. Finally, hydrogels, magneto-reactive materials, members of the National System of Researchers (Sistema
and compositions containing monomers were utilized in Nacional de Investigadores).
the fabrication of biocompatible, sustainable, and cost-
effective innovative bioinks and bionanoinks in order to Conflict of interest
improve their bioactivity and durability. In the “printing The authors declare no conflict of interest.
methods” category, the effects of the process parameters,
including nozzle temperature, extrusion rate, and fiber Author contributions
orientation, have significant impact on the deformation,
fiber orientation, fixing ratio, and shape recovery process Conceptualization: Angelica A. Martinez-De-Anda,
of the structure. Cell-friendly bioprinting methods have Marisela Rodriguez-Salvador, Pedro F. Castillo-Valdez
potential uses in the fabrication of 3D cellular structures, Formal analysis: Angelica A. Martinez-De-Anda
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 195 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1112