Page 202 - IJB-9-6
P. 202
International Journal of Bioprinting Attractiveness of 4D printing in medical field
Figure 3. (a) Diagram of stomatal response to temperature and
(b) PNIPAM hydrogel network. (Adapted from Zu et al. (2022) )
[64]
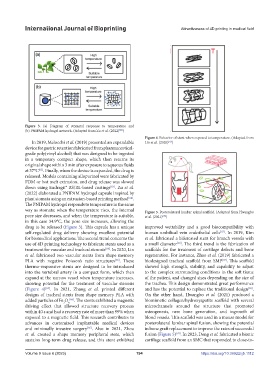
Figure 4. Behavior of stent when exposed to temperature. (Adapted from
In 2019, Melocchi et al. (2019) presented an expandable Lin et al. (2020) )
[65]
device for gastric retention fabricated from pharmaceutical-
grade poly(vinyl alcohol) that was designed to be ingested
in a temporary compact shape, which then returns its
original shape within 3 min after exposure to aqueous fluids
at 37°C . Finally, when the device is expanded, the drug is
[63]
released. Models containing allopurinol were fabricated by
FDM or hot melt extrusion, and drug release was slowed
down using Eudragit® RS/RL-based coatings . Zu et al.
[63]
(2022) elaborated a PNIPAM hydrogel capsule inspired by
plant stomata using an extrusion-based printing method .
[64]
The PNIPAM hydrogel responds to temperature in the same
way as stomata; when the temperature rises, the internal Figure 5. Posterolateral lumbar spinal scaffold. (Adapted from Hwangbo
pore size decreases, and when the temperature is suitable, et al. (2021) )
[70]
in this case 34.9°C, the pore size increases, allowing the
drug to be released (Figure 3). This capsule has a unique improved wettability and a good biocompatibility with
[67]
self-regulated drug delivery showing excellent potential human umbilical vein endothelial cells . In 2019, Kim
for biomedical applications. The second trend concerns the et al. fabricated a bifurcated stent for branch vessels with
[68]
use of 4D printing technology to fabricate stents used as a a small diameter . The third trend is the fabrication of
treatment for vascular and tracheal stenosis . In 2020, Lin scaffolds for the treatment of cartilage defects and bone
[64]
et al. fabricated two vascular stents from shape memory regeneration. For instance, Zhao et al. (2019) fabricated a
PLA with negative Poisson’s ratio structures . These biodesigned tracheal scaffold from SMP . This scaffold
[69]
[65]
thermo-responsive stents are designed to be introduced showed high strength, stability, and capability to adjust
into the vertebral artery in a compact form, which then to the complex surrounding conditions in the soft tissue
expand at the narrow vessel when temperature increases, of the patient, and changed sizes depending on the size of
showing potential for the treatment of vascular stenosis the trachea. This design demonstrated great performance
[69]
(Figure 4) . In 2021, Zhang et al. printed different and has the potential to replace the traditional design .
[65]
designs of tracheal stents from shape memory PLA with On the other hand, Hwangbo et al. (2021) produced a
added particles of Fe O 4 [66] . The stents exhibited a magnetic biomimetic collagen/hydroxyapatite scaffold with several
3
driving effect that allowed structure recovery process microchannels around the structure that promoted
within 40 s and had a recovery rate of more than 99% when osteogenesis, new bone generation, and ingrowth of
exposed to a magnetic field. This research contributes to blood vessels. This scaffold was used in a mouse model for
advances in customized implantable medical devices posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion, showing the potential
and minimally invasive surgery . Also in 2021, Zhou in bone graft replacement to improve the rates of successful
[66]
et al. created a shape memory peripheral stent, which fusion (Figure 5) . In 2023, Deng et al. fabricated a bionic
[70]
sustains long-term drug release, and this stent exhibited cartilage scaffold from an SMC that responded to close-to-
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 194 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1112