Page 408 - IJB-9-6
P. 408
International Journal of Bioprinting Biofabrication for islet transplantation
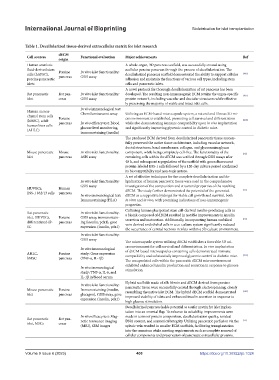
Table 1. Decellularized tissue-derived extracellular matrix for islet research
dECM
Cell sources Functional evaluation Major achievements Ref
origin
Human amniotic A whole organ, 3D pancreas scaffold, was successfully created using
fluid-derived stem Porcine In vitro islet functionality: acellular porcine pancreas through the process of decellularization. The
cells (hAFSC), pancreas GSIS assay decellularized pancreas scaffold demonstrated the ability to support cellular [106]
porcine pancreatic adhesion and maintain the functions of various cell types, including stem
islets cells and pancreatic islets.
A novel protocol for thorough decellularization of rat pancreas has been
Rat pancreatic Rat pan- In vitro islet functionality: developed. The resulting non-immunogenic ECM retains the organ-specific [107]
islet creas GSIS assay protein network, including vascular and ductular structures while effective-
ly preserving the majority of viable and intact islet cells.
In vivo immunological test:
Human mesen- Chemiluminescent array Utilizing an ECM-based microcapsule system, a natural and fibrous 3D mi-
chymal stem cells Porcine croenvironment is established, promoting cell survival and differentiation
(hMSC), adult pancreas In vivo efficacy test: Blood while also demonstrating immune compatibility upon in vivo implantation [108]
human liver cells glucose level monitoring, and significantly improving glycemic control in diabetic mice.
(AHLC)
immunostaining (insulin)
The produced ECM derived from decellularized pancreatic tissue success-
fully preserved the native tissue architecture, including vascular network,
ductal structures, basal membranes, collagen, and glycosaminoglycan
Mouse pancreatic Mouse In vitro islet functionality: component, while being completely cell-free. The functionality of the [72]
islet pancreas ASIS assay remaining cells within the dECM was verified through GSIS assays after
48 h, and subsequent repopulation of the scaffold with green fluorescent
protein-labeled INS-1 cells followed by a 120-day culture period confirmed
its biocompatibility and non-toxic nature.
A set of effective techniques for the complete decellularization and de-
In vitro islet functionality: lipidization of human pancreatic tissue were used in the comprehensive
GSIS assay investigation of the composition and structural properties of the resulting
HUVECs, Human dECM. The study further demonstrated the potential of the generated [73]
INS-1 832/13 cells pancreas
In vivo immunological test: dECM as a supportive hydrogel for viable cell growth and survival, both
Immunostaining (HLA) in vitro and in vivo, with promising indications of non-immunogenic
properties.
Culturing human pluripotent stem cell-derived insulin-producing cells in
Rat pancreatic In vitro islet functionality: a bioink composed of dECM resulted in notable improvements in insulin
islet, HUVECs, Porcine GSIS assay, immunostain- secretion and maturation. Additionally, incorporating human umbilical [71]
differentiated-iP- pancreas ing (insulin, pdx1), gene vein-derived endothelial cells in a co-culture system significantly reduced
SC expression (insulin, pdx1)
the occurrence of central necrosis in islets within a 3D culture environment.
In vitro islet functionality:
GSIS assay
The microcapsule system utilizing dECM establishes a favorable 3D mi-
croenvironment for cell survival and differentiation. In vivo implantation
In vitro immunological
AHLC, Porcine study: Gene expression of dECM-based microcapsules containing cells demonstrated immune [109]
compatibility and substantially improved glycemic control in diabetic mice.
hMSC pancreas (TNF-α, IL-1β)
The encapsulated cells within the pancreatic dECM microenvironment
exhibited enhanced insulin production and secretion in response to glucose
In vivo immunological stimulation.
study: TNF-α, IL-6, and
IL-1β in blood serum
Hybrid scaffolds made of silk fibroin and dECM derived from porcine
In vitro islet functionality:
Mouse pancreatic Porcine Immunostaining (insulin, pancreatic tissue were successfully created through electrospinning, closely [110]
resembling the native islet ECM. The hybrid dECM scaffold demonstrated
islet pancreas glucagon), GSIS assay, gene improved viability of islets and enhanced insulin secretion in response to
expression (insulin, pdx1)
high glucose stimulation.
Decellularized pancreas holds potential as a safer matrix for islet implan-
tation into an omental flap. To enhance its suitability, improvements were
In vivo efficacy test: Mag- made in terms of protein composition, decellularization quality, residual
Rat pancreatic Rat pan- netic resonance imaging DNA content, and anatomical integrity. Utilizing pancreatic perfusion via the [74]
islet, MSCs creas
(MRI), SEM images splenic vein resulted in smaller ECM scaffolds, facilitating transplantation
into the omentum while meeting requirements such as complete removal of
cellular components and preservation of pancreatic extracellular proteins.
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 400 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1024