Page 411 - IJB-9-6
P. 411
International Journal of Bioprinting Biofabrication for islet transplantation
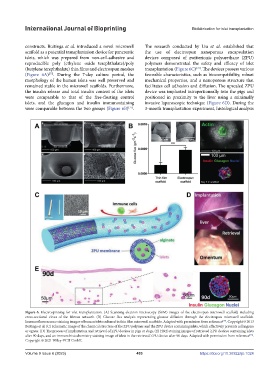
constructs. Buitinga et al. introduced a novel microwell The research conducted by Liu et al. established that
scaffold as a potential transplantation device for pancreatic the use of electrospun nanoporous encapsulation
islets, which was prepared from non-cell-adhesive and devices composed of zwitterionic polyurethane (ZPU)
reproducible poly (ethylene oxide terephthalate)/poly polymers demonstrated the safety and efficacy of islet
(butylene terephthalate) thin films and electrospun meshes transplantation (Figure 6C) . The devices possess various
[78]
(Figure 6A) . During the 7-day culture period, the favorable characteristics, such as biocompatibility, robust
[77]
morphology of the human islets was well preserved and mechanical properties, and a nanoporous structure that
remained stable in the microwell scaffolds. Furthermore, facilitates cell adhesion and diffusion. The upscaled ZPU
the insulin release and total insulin content of the islets device was implanted intraperitoneally into the pigs and
were comparable to that of the free-floating control positioned in proximity to the liver using a minimally
islets, and the glucagon and insulin immunostaining invasive laparoscopic technique (Figure 6D). During the
were comparable between the two groups (Figure 6B) . 3-month transplantation experiment, histological analysis
[77]
Figure 6. Electrospinning for islet transplantation. (A) Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the electrospun microwell scaffold, including
cross-sectional views of the fibrous network. (B) Glucose flux analysis representing glucose diffusion through the electrospun microwell scaffolds.
Immunofluorescence staining images of human islets cultured in thin film microwell scaffolds. Adapted with permission from reference . Copyright © 2013
[77]
Buitinga et al. (C) Schematic image of the chemical structure of the ZPU polymer and the ZPU device containing islets, which effectively prevents cell ingress
or egress. (D) The process of implantation and retrieval of ZPU devices in pigs or dogs. (E) H&E staining images of retrieved ZPU devices containing islets
after 90 days, and an immunohistochemistry staining image of islets in the retrieved ZPU device after 90 days. Adapted with permission from reference .
[78]
Copyright © 2021 Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 403 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.1024