Page 75 - IJB-9-6
P. 75
International Journal of Bioprinting 3D Aerosol Jet® printing for microstructuring
a b
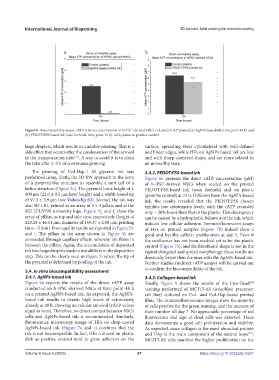
Figure 6. Biocompatibility assays. rATP relative concentration of h-iPSC-derived NSCs cultured on AJ® printed (a) AgNPs-based ink (time point 48 h) and
(b) PEDOT:PSS-based ink (own formula, time point 72 h), with plastic as positive control.
large droplets, which results in unstable printing. This is a surface, spreading their cytoskeletal with well-defined
side effect that occurs after the condensation of the aerosol and linear edges, while HFs on AgNPs-based ink are less
[33]
in the transportation tube . A way to avoid it is to clean and with sharp-cornered shape, and are more related to
the tube after 2–3 h of continuous printing. an unhealthy state.
The printing of Col-Hap-1 M glycerol ink was 3.4.2. PEDOT:PSS-based ink
performed using, firstly, the 3D-PW approach in the form Figure 6b presents the direct rATP concentration (µM)
of a pyramid-like structure to resemble a unit cell of a of h-iPSC-derived NSCs when seeded on the printed
lattice structure (Figure 5e). The pyramid has a height of ± PEDOT:PSS-based ink (own formula) and on plastic
400 µm (22.0 ± 0.5 µm layer height) and a width-based tip (positive control) at 72 h. Different from the AgNPs-based
of 97.3 ± 3.9 µm (see Videoclip S3). Second, the ink was ink, the results revealed that the PEDOT:PSS chosen
also 3D-LBL-printed as an array of 3 × 3 pillars and as the exhibits low cytotoxicity levels, with the rATP recorded
KU LEUVEN university logo. Figure 5f and f show the only ~ 20% lower than that of the plastic. This discrepancy
2
1
array of pillars, as top and side view, respectively (height of can be caused by a hydrophobic behavior of the ink, which
223.28 ± 46.51 µm, diameter of 159.37 ± 2.98 µm, printing induces low cellular adhesion. Immunofluorescent assays
time ~ 5 min). Poor-quality results are reported in Figure 5h of HFs on printed samples (Figure 7b) indeed show a
and i. The pillars in the array shown in Figure 5h are good and healthy cellular proliferation at day 5. Even if
connected through capillary effects, whereby ink flows in the confluence has not been reached yet as for the plastic
between the pillars. Again, the accumulation of deposited control (Figure 7b), and the fibroblasts’ shape is not in the
ink into large droplets leads to instabilities in the deposition typical elongated and spread morphology, these results are
step. This can be clearly seen in Figure 5i where the tip of drastically better than the ones with the AgNPs-based ink.
the pyramid is deformed by pooling of the ink. Further studies (indirect rATP assays) will be carried out
to confirm the biocompatibility of the ink.
3.4. In vitro biocompatibility assessment
3.4.1. AgNPs-based ink 3.4.3. Collagen-based ink
Figure 6a reports the results of the direct rATP assay Finally, Figure 8 shows the results of the Live-Dead
TM
conducted on h-iPSC-derived NSCs at time point 48 h staining performed of MC3T3-E1 (osteoblast precursor
on a printed AgNPs-based ink. As expected, the AgNPs- cell line) cultured on Col- and Col-Hap-based printed
based ink results in drastic high levels of cytotoxicity films. The immunofluorescence images show the majority
already at 48 h, showing no cellular survival (rATP values of cells positive for the green staining, and the increase of
equal to zero). Therefore, no direct contact between NSCs their number till day 7. No appreciable percentage of red
cells and AgNPs-based ink is recommended. Similarly, fluorescence and sign of dead cells was detected. These
fluorescence microscopy image of HFs on drop-casted data demonstrate a good cell proliferation and viability.
AgNPs-based ink (Figure 7a and c) confirms that the As expected, since collagen is the most abundant protein
ink is not biocompatible. In fact, HFs cultured on plastic and HAp is the main component of the natural bone ,
[49]
dish as positive control tend to grow adherent on the MC3T3-E1 cells manifest the higher proliferation on the
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 67 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0257