Page 85 - IJB-9-6
P. 85
International Journal of Bioprinting Review of 3D bioprinted organoids
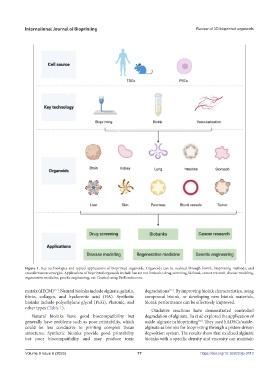
Figure 1. Key technologies and typical applications of bioprinted organoids. Organoids can be realized through bioink, bioprinting methods, and
vascularization strategies. Applications of bioprinted organoids include but are not limited to drug screening, biobank, cancer research, disease modeling,
regenerative medicine, genetic engineering, etc. Created using BioRender.com.
[15]
[17]
matrix (dECM) . Natural bioinks include alginate, gelatin, degradations . By improving bioink characteristics, using
fibrin, collagen, and hyaluronic acid (HA). Synthetic compound bioink, or developing new bioink materials,
bioinks include polyethylene glycol (PEG), Pluronic, and bioink performance can be effectively improved.
other types (Table 1). Oxidative reactions have demonstrated controlled
Natural bioinks have good biocompatibility but degradation of alginate. Jia et al. explored the application of
generally have problems such as poor printability, which oxide-alginate in bioprinting . They used hADSCs/oxide-
[36]
could be less conducive to printing complex tissue alginate as bioinks for bioprinting through a piston-driven
structures. Synthetic bioinks provide good printability deposition system. The results show that oxidized alginate
but poor biocompatibility and may produce toxic bioinks with a specific density and viscosity can maintain
Volume 9 Issue 6 (2023) 77 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0112