Page 243 - v11i4
P. 243
International Journal of Bioprinting Fine collagen scaffold for osteogenesis
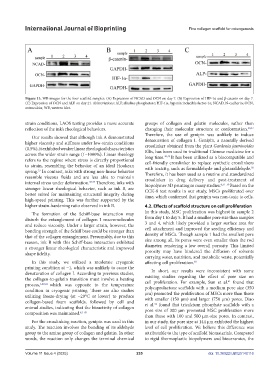
Figure 13. WB images for the four scaffold samples. (A) Expression of NCAD and OCN on day 7. (B) Expression of HIF-1α and β-catenin on day 7.
(C) Expression of OCN and ALP on day 21. Abbreviations: ALP, alkaline phosphatase; HIF-1α, hypoxia inducible factor-1α; NCAD, N-cadherin; OCN,
osteocalcin; WB, western blot.
strain conditions, LAOS testing provides a more accurate groups of collagen and gelatin molecules, rather than
reflection of the ink’s rheological behaviors. changing their molecular structure or conformation. 46,47
Therefore, the use of genipin was unlikely to induce
Our results showed that although ink A demonstrated
higher viscosity and stiffness under low-strain conditions denaturation of collagen I. Genipin, a naturally derived
crosslinker obtained from the plant Gardenia jasminoides
(0.5%), it exhibited weaker linear rheological characteristics Ellis, has been used in traditional Chinese medicine for a
across the wider strain range (1–1000%). Linear rheology long time. 48,49 It has been utilized as a biocompatible and
refers to the regime where stress is directly proportional cell-friendly crosslinker to replace synthetic crosslinkers
to strain, resembling the behavior of an ideal Hookean with toxicity, such as formaldehyde and glutaraldehyde. 50
spring. In contrast, inks with strong non-linear behavior Therefore, it has been used as a routine and standardized
37
resemble viscous fluids and are less able to maintain crosslinker in drug delivery and post-treatment of
internal stress under deformation. 38,39 Therefore, inks with biopolymer 3D printing in many studies. 6,51–59 Based on the
stronger linear rheological behavior, such as ink B, are CCK-8 test results in our study, MSCs proliferated over
better suited for maintaining structural integrity during time, which confirmed that genipin was non-toxic to cells.
high-speed printing. This was further supported by the
higher strain-hardening ratio observed in ink B. 4.2. Effects of scaffold structure on cell proliferation
The formation of the Schiff-base interaction may In this study, MSC proliferation was highest in sample 2
disturb the entanglement of collagen I macromolecules from day 1 to day 5. It had a smaller pore size than samples
and reduce viscosity. Under a larger strain, however, the 3 and 4, which likely provided a larger surface area for
bonding strength of the Schiff base could be stronger than cell attachment and improved the seeding efficiency and
that of the collagen entanglement. Presumably, due to this density of MSCs. Though sample 1 had the smallest pore
reason, ink B with this Schiff-base interaction exhibited size among all, its pores were even smaller than the rod
a stronger linear rheological characteristic and improved diameter, rendering a low overall porosity. This limited
shape fidelity. porosity may have hindered the diffusion of solvents
carrying water, nutrition, and metabolic waste, potentially
In this study, we utilized a moderate cryogenic affecting cell proliferation. 60
printing condition at −1, which was unlikely to cause the
denaturation of collagen I. According to previous studies, In short, our results were inconsistent with some
the collagen-to-gelatin transition must involve a heating existing studies regarding the effect of pore size on
61
process, 1,40,41 which was opposite to the temperature cell proliferation. For example, Sun et al. found that
condition in cryogenic printing. There are also studies polycaprolactone scaffolds with a medium pore size (350
μm) promoted the proliferation of MSCs more than those
utilizing freeze-drying (at −20°C or lower) to produce with smaller (150 μm) and larger (750 μm) pores. Diao
collagen-based foam scaffolds, followed by cell and et al. found that tricalcium phosphate scaffolds with a
62
animal studies, indicating that the bioactivity of collagen pore size of 300 μm promoted MSC proliferation more
composition was maintained. 42–45
than those with 100 and 500 μm-size pores. In contrast,
For the crosslinking reaction, genipin was used in this in our study, the pore size at 144 μm exhibited the highest
study. The reaction involves the bonding of its aldehyde level of cell proliferation. We believe this difference was
group to the amine group of collagen and gelatin. In other attributable to the type of scaffold biomaterials. Compared
words, the reaction only changes the terminal chemical to rigid thermoplastic biopolymers and bioceramics, the
Volume 11 Issue 4 (2025) 235 doi: 10.36922/IJB025140116