Page 179 - IJOCTA-15-1
P. 179
Recent metaheuristics on control parameter determination
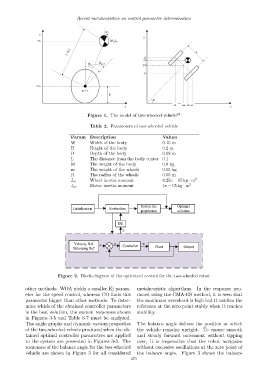
Figure 1. The model of two-wheeled vehicle 38
Table 2. Parameters of two-wheeled vehicle
Param Description Values
W Width of the body 0.15 m
H Height of the body 0.2 m
D Depth of the body 0.08 m
L The distance from the body center 0.1
M The weight of the body 0.8 kg
m The weight of the wheels 0.05 kg
R The radius of the wheels 0.05 m
Wheel inertia moment 6.25e − 05 kg · m 2
J w
Motor inertia moment 1e − 05 kg · m 2
J m
Figure 2. Block-diagram of the optimized control for the two-wheeled robot
other methods. WOA yields a smaller Ki param- metaheuristic algorithms. In the response pro-
eter for the speed control, whereas CO finds this duced using the CMA-ES method, it is seen that
parameter bigger than other methods. To deter- the maximum overshoot is high but it catches the
mine which of the obtained controller parameters reference at the zero point stably when it reaches
is the best solution, the system responses shown stability.
in Figures 3-5 and Table 6-7 must be analyzed.
The angle graphs and dynamic system properties The balance angle defines the position at which
of the two-wheeled vehicle produced when the ob- the vehicle remains upright. To ensure smooth
tained optimal controller parameters are applied and steady forward movement without tipping
to the system are presented in Figures 3-5. The over, it is imperative that the robot navigates
responses of the balance angle for the two-wheeled without excessive oscillations at the zero point of
vehicle are shown in Figure 3 for all considered the balance angle. Figure 3 shows the balance
173