Page 81 - IJPS-11-6
P. 81
International Journal of
Population Studies The paradox of urban decline in India
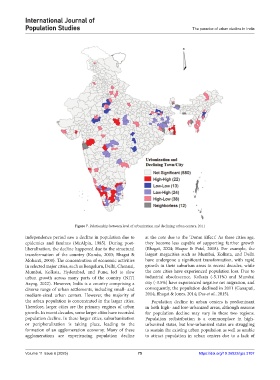
Figure 7. Relationship between level of urbanization and declining urban centers, 2011
independence period saw a decline in population due to at the core due to the ‘Donut Effect.’ As these cities age,
epidemics and famines (McAlpin, 1985). During post- they become less capable of supporting further growth
liberalization, the decline happened due to the structural (Bhagat, 2004; Haque & Patel, 2018). For example, the
transformation of the country (Kundu, 2003; Bhagat & largest megacities such as Mumbai, Kolkata, and Delhi
Mohanti, 2008). The concentration of economic activities have undergone a significant transformation, with rapid
in selected major cities, such as Bengaluru, Delhi, Chennai, growth in their suburban areas in recent decades, while
Mumbai, Kolkata, Hyderabad, and Pune, led to slow the core cities have experienced population loss. Due to
urban growth across many parts of the country (NITI industrial obsolescence, Kolkata (-5.11%) and Mumbai
Aayog, 2022). However, India is a country comprising a city (-3.5%) have experienced negative net migration, and
diverse range of urban settlements, including small- and consequently, the population declined in 2011 (Ganapati,
medium-sized urban centers. However, the majority of 2014; Bhagat & Jones, 2014; Das et al., 2015).
the urban population is concentrated in the larger cities. Population decline in urban centers is predominant
Therefore, larger cities are the primary engines of urban in both high- and low-urbanized areas, although reasons
growth. In recent decades, some larger cities have recorded for population decline may vary in these two regions.
population decline. In these larger cities, suburbanization Population redistribution is a commonplace in high-
or peripheralization is taking place, leading to the urbanized states, but low-urbanized states are struggling
formation of an agglomeration economy. Many of these to sustain the existing urban population as well as unable
agglomerations are experiencing population decline to attract population in urban centers due to a lack of
Volume 11 Issue 6 (2025) 75 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijps.3107