Page 87 - ITPS-7-1
P. 87
INNOSC Theranostics and
Pharmacological Sciences PfHSP and polyamines interactions
A B
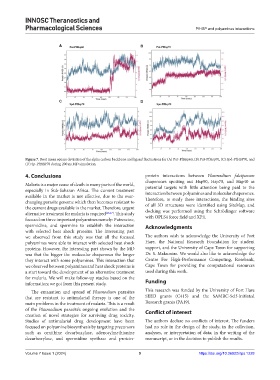
C D
Figure 7. Root mean square deviation of the alpha carbon backbone and ligand fluctuations for (A) Put-PfHsp60, (B) Put-PfHsp70, (C) Spd-PfHSP70, and
(D) Sp-PfHSP70 during 200 ns MD simulation.
4. Conclusions protein interactions between Plasmodium falciparum
chaperones spotting out Hsp90, Hsp70, and Hsp40 as
Malaria is a major cause of death in many parts of the world, potential targets with little attention being paid to the
especially in Sub-Saharan Africa. The current treatment interaction between polyamines and molecular chaperones.
available in the market is not effective, due to the ever-
changing parasite genome which then becomes resistant to Therefore, to study these interactions, the binding sites
of all 3D structures were identified using SiteMap, and
the current drugs available in the market. Therefore, urgent
alternative treatment for malaria is required [26,27] . This study docking was performed using the Schrödinger software
focused on three important polyamines namely: Putrescine, with OPLS4 force field and XP.1.
spermidine, and spermine to establish the interaction Acknowledgments
with selected heat shock proteins. The interesting part
we observed from this study was that all the focused The authors wish to acknowledge the University of Fort
polyamines were able to interact with selected heat shock Hare, the National Research Foundation for student
proteins. However, the interesting part shown by the MD support, and the University of Cape Town for supporting
was that the bigger the molecular chaperones the longer Dr. S. Makumire. We would also like to acknowledge the
they interact with some polyamines. This interaction that Centre For High-Performance Computing, Rosebank,
we observed between polyamines and heat shock proteins is Cape Town for providing the computational resources
a start toward the development of an alternative treatment used during this work.
for malaria. We will make follow-up studies based on the
information; we got from this present study. Funding
The emanation and spread of Plasmodium parasites This research was funded by the University of Fort Hare
that are resistant to antimalarial therapy is one of the SEED grants (C415) and the SAMRC-Self-Initiated
main problems in the treatment of malaria. This is a result Research grants (PA19).
of the Plasmodium parasite’s ongoing evolution and the Conflict of interest
creation of novel strategies for surviving drug toxicity.
Studies of antimalarial drug development have been The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders
focused on polyamine biosynthesis by targeting precursors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection,
such as ornithine decarboxylase, adenosylmethionine analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the
decarboxylase, and spermidine synthase and protein- manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Volume 7 Issue 1 (2024) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/itps.1228