Page 71 - JCTR-11-2
P. 71
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Fetal posterior fossa imaging findings
A B A B
C D
C D
E F
Figure 4. Normal MRI images. (A and B) Sagittal TRUFI MRI images
of a 30-week fetus depicting the relationship between the brainstem and
vermis, vermian lobulation, and the tegmentovermian angle. (C and D)
Sagittal TRUFI MRI images of a 22-week fetus showing the craniocaudal
diameter of the vermis.
Abbreviations: MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; TRUFI: True fast
imaging with steady-state precession.
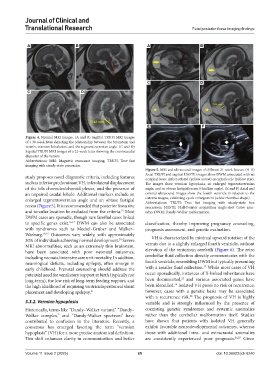
Figure 5. MRI and ultrasound images of different 21-week fetuses. (A-D)
Axial TRUFI and sagittal HASTE images show DWM associated with an
study proposes novel diagnostic criteria, including features occipital bone defect-related (yellow arrow) encephalocele (yellow star).
such as inferior predominant VH, inferolateral displacement The images show vermian hypoplasia, an enlarged tegmentovermian
of the tela choroidea/choroid plexus, and the presence of angle, and an obtuse fastigial recess (thin line angle). (E and F) Axial and
an unpaired caudal lobule. Additional markers include an coronal ultrasound images show the fourth ventricle in relation to the
enlarged tegmentovermian angle and an obtuse fastigial cisterna magna, exhibiting cystic enlargement (white rhombus shape).
Abbreviations: TRUFI: True fast imaging with steady-state free
recess (Figure 5). It is recommended that posterior fossa size precession; HASTE: Half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-
and torcular location be excluded from the criteria. Most echo; DWM: Dandy-Walker malformation.
15
DWM cases are sporadic, though rare familial cases linked
to specific genes exist. 16,17 DWM can also be associated classification, thereby improving pregnancy counseling,
with syndromes such as Meckel–Gruber and Walker– prognosis assessment, and genetic evaluation.
Warburg. 18,19 Outcomes vary widely, with approximately
30% of individuals achieving normal development. Severe VH is characterized by minimal upward rotation of the
20
MRI abnormalities, such as an extremely thin brainstem, vermis due to a slightly enlarged fourth ventricle, without
have been associated with poor neonatal outcomes, elevation of the tentorium cerebelli (Figure 6). The retro
including neonatal intensive care unit mortality. In addition, cerebellar fluid collection directly communicates with the
neurological deficits, including epilepsy, often emerge in fourth ventricle, resembling DWM but typically presenting
22
early childhood. Prenatal counseling should address the with a smaller fluid collection. While most cases of VH
potential need for ventilatory support at birth (typically not occur sporadically, instances of X-linked inheritance have
23
long-term), the low risk of long-term feeding support, and been documented, and various associated genes have
24
the high likelihood of requiring ventriculoperitoneal shunt been identified. Isolated VH poses no risk of recurrence;
placement and developing epilepsy. 21 however, cases with a genetic basis may be associated
with a recurrence risk. The prognosis of VH is highly
25
3.3.2. Vermian hypoplasia variable and is strongly influenced by the presence of
Historically, terms like “Dandy–Walker variant,” “Dandy– coexisting genetic syndromes and systemic anomalies
Walker complex,” and “Dandy-Walker spectrum” have rather than the cerebellar malformation itself. Studies
contributed to confusion in the literature. Recently, a have shown that patients with isolated VH generally
consensus has emerged favoring the term “vermian exhibit favorable neurodevelopmental outcomes, whereas
hypoplasia” (VH) for a more precise anatomical definition. those with additional intra- and extracranial anomalies
This shift enhances clarity in communication and better are consistently experienced poor prognosis. 26,27 Given
Volume 11 Issue 2 (2025) 65 doi: 10.36922/jctr.6240