Page 75 - JCTR-11-2
P. 75
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Fetal posterior fossa imaging findings
A B
C D E
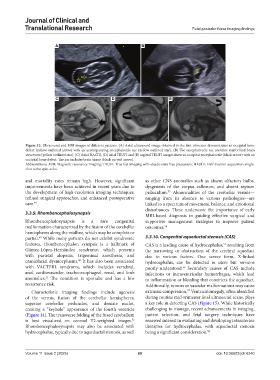
Figure 13. Ultrasound and MRI images of different patients. (A) Axial ultrasound image obtained in the first trimester demonstrates an occipital bone
defect (yellow outlined arrow) with an accompanying encephalocele sac (yellow outlined star). (B) The encephalocele sac contains malformed brain
structures (yellow outlined star). (C) Axial HASTE, (D) axial TRUFI and (E) sagittal TRUFI images show an occipital encephalocele (black arrow) with an
occipital bone defect. The sac includes brain tissue (black curved arrow).
Abbreviations: MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; TRUFI: True fast imaging with steady-state free precession; HASTE: Half-Fourier acquisition single-
shot turbo spin-echo.
and mortality rates remain high. However, significant as other CNS anomalies such as absent olfactory bulbs,
improvements have been achieved in recent years due to dysgenesis of the corpus callosum, and absent septum
the development of high-resolution imaging techniques, pellucidum. Abnormalities of the cerebellar vermis—
53
refined surgical approaches, and enhanced postoperative ranging from its absence to various pathologies—are
care. 48 linked to a spectrum of movement, balance, and emotional
disturbances. These underscore the importance of early
3.3.9. Rhombencephalosynapsis
MRI-based diagnosis in guiding effective surgical and
Rhombencephalosynapsis is a rare congenital supportive management strategies to improve patient
malformation characterized by the fusion of the cerebellar outcomes. 54
hemispheres along the midline, which may be complete or
partial. While many patients do not exhibit syndromic 3.3.10. Congenital aqueductal stenosis (CAS)
49
features, rhombencephalon synapsis is a hallmark of CAS is a leading cause of hydrocephalus, resulting from
55
Gómez-López-Hernández syndrome, which presents the narrowing or obstruction of the cerebral aqueduct
with parietal alopecia, trigeminal anesthesia, and due to various factors. One severe form, X-linked
craniofacial dysmorphisms. It has also been associated hydrocephalus, can be detected in utero but remains
50
with VACTERL syndrome, which includes vertebral, poorly understood. Secondary causes of CAS include
56
anal, cardiovascular, tracheoesophageal, renal, and limb infections or intraventricular hemorrhages, which lead
anomalies. The condition is sporadic and has a low to inflammation or bleeding that constricts the aqueduct.
51
recurrence risk. Additionally, tumors or vascular malformations may cause
57
Characteristic imaging findings include agenesis extrinsic compression. Ventriculomegaly, often identified
of the vermis, fusion of the cerebellar hemispheres, during routine mid-trimester fetal ultrasound scans, plays
superior cerebellar peduncles, and dentate nuclei, a key role in detecting CAS (Figure 15). While historically
creating a “keyhole” appearance of the fourth ventricle challenging to manage, recent advancements in imaging,
(Figure 14). The transverse folding of the fused cerebellum patient selection, and fetal surgery techniques have
is best visualized on coronal T2-weighted images. renewed interest in evaluating and developing intrauterine
52
Rhombencephalosynapsis may also be associated with therapies for hydrocephalus, with aqueductal stenosis
hydrocephalus, typically due to aqueductal stenosis, as well being a significant consideration. 58
Volume 11 Issue 2 (2025) 69 doi: 10.36922/jctr.6240