Page 77 - JCTR-11-2
P. 77
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Fetal posterior fossa imaging findings
A B A B
C D
C
E F
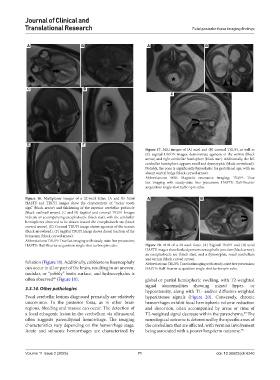
Figure 17. MRI images of (A) axial and (B) coronal TRUFI, as well as
(C) sagittal HASTE images, demonstrate agenesis of the vermis (black
arrow) and right cerebellar hemisphere (black star). Additionally, the left
cerebellar hemisphere appears small and dysmorphic (black arrowhead).
Notably, the pons is significantly hypoplastic for gestational age, with an
absent ventral bulge (black curved arrow).
Abbreviations: MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; TRUFI: True
fast imaging with steady-state free precession; HASTE: Half-Fourier
acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo.
Figure 16. Multiplanar images of a 22-week fetus. (A and B) Axial A B
HASTE and TRUFI images show the characteristic of “molar tooth
sign” (black arrow) and thickening of the superior cerebellar peduncle
(black outlined arrow). (C and D) Sagittal and coronal TRUFI İmages
indicate an accompanying encephalocele (black star), with the cerebellar
hemispheres observed to be drawn toward the encephalocele sac (black
curved arrow). (E) Coronal TRUFI image shows agenesis of the vermis
(black arrowhead). (F) Sagittal TRUFI image shows dorsal traction of the
brainstem (black curved arrow).
Abbreviations: TRUFI: True fast imaging with steady-state free precession;
HASTE: Half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo. Figure 18. MRI of a 20-week fetus. (A) Sagittal TRUFI and (B) axial
HASTE images show kinked pontomesencephalic junction (black arrow),
an encephalocele sac (black star), and a dysmorphic, small cerebellum
and vermis (black curved arrow).
foliation (Figure 18). Additinally, cobblestone lissencephaly Abbreviations: TRUFI: True fast imaging with steady-state free precession;
can occur in all or part of the brain, resulting in an uneven, HASTE: Half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo.
nodular, or “pebbly” brain surface, and hydrocephalus is
often observed (Figure 19). global or partial hemispheric swelling, with T2-weighted
68
signal abnormalities showing mixed hyper- or
3.3.14. Other pathologies hypointensity, along with T1- and/or diffusion-weighted
Focal cerebellar lesions diagnosed prenatally are relatively hyperintense signals (Figure 20). Conversely, chronic
uncommon. In the posterior fossa, as in other brain hemorrhages exhibit focal hemispheric volume reduction
regions, bleeding and masses can occur. The detection of and distortion, often accompanied by areas or rims of
a focal echogenic lesion in the cerebellum via ultrasound T2-weighted signal decrease within the parenchyma. The
69
often suggests parenchymal hemorrhage. The imaging neurological outcome is determined by the specific areas of
characteristics vary depending on the hemorrhage stage. the cerebellum that are affected, with vermian involvement
Acute and subacute hemorrhages are characterized by being associated with a poorer long-term outcome. 70
Volume 11 Issue 2 (2025) 71 doi: 10.36922/jctr.6240