Page 72 - JCTR-11-2
P. 72
Journal of Clinical and
Translational Research Fetal posterior fossa imaging findings
A B A B
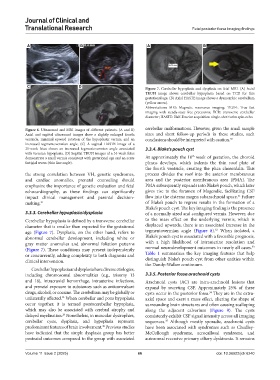
C D Figure 7. Cerebellar hypoplasia and dysplasia on fetal MRI. (A) Axial
TRUFI image shows cerebellar hypoplasia based on TCD for this
gestational age. (B) Axial HASTE image shows a dysmorphic cerebellum
(yellow arrow).
Abbreviations: MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; TRUFI: True fast
imaging with steady-state free precession; TCD: transverse cerebellar
diameter; HASTE: Half-Fourier acquisition single-shot turbo spin-echo.
Figure 6. Ultrasound and MRI images of different patients. (A and B) cerebellar malformations. However, given the small sample
Axial and sagittal ultrasound images show a slightly enlarged fourth sizes and short follow-up periods in these studies, such
ventricle, minimal upward rotation of the hypoplastic vermis, and an conclusions should be interpreted with caution. 28
increased tegmentovermian angle. (C) A sagittal HASTE image of a
21-week fetus shows an increased tegmentovermian angle associated 3.3.4. Blake’s pouch cyst
with vermian hypoplasia. (D) Sagittal TRUFI images of a 34-week fetus
th
demonstrate a small vermis consistent with gestational age and an acute At approximately the 10 week of gestation, the choroid
fastigial recess (thin line angle). plexus develops, which indents the thin roof plate of
the fourth ventricle, creating the plica choroidalis. This
the strong correlation between VH, genetic syndromes, process divides the roof into the anterior membranous
and cardiac anomalies, prenatal counseling should area and the posterior membranous area (PMA). The
emphasize the importance of genetic evaluation and fetal PMA subsequently expands into Blake’s pouch, which later
echocardiography, as these findings can significantly gives rise to the foramen of Magendie, facilitating CSF
31
impact clinical management and parental decision- flow into the cisterna magna subarachnoid space. Failure
making. 21 of Blake’s pouch to regress results in the formation of a
Blake’s pouch cyst. The key imaging finding is the presence
3.3.3. Cerebellar hypoplasia/dysplasia of a normally sized and configured vermis. However, due
Cerebellar hypoplasia is defined by a transverse cerebellar to the mass effect on the underlying vermis, which is
diameter that is smaller than expected for the gestational displaced upwards, there is an associated increase in the
32
age (Figure 7). Dysplasia, on the other hand, refers to tegmentovermian angle (Figure 8). When isolated, a
abnormal cerebellar development, including white or Blake’s pouch cyst is associated with a favorable prognosis,
gray matter anomalies and abnormal foliation patterns with a high likelihood of intrauterine resolution and
33
(Figure 7). These conditions may present independently normal neurodevelopment outcomes in nearly all cases.
or concurrently, adding complexity to both diagnosis and Table 1 summarizes the key imaging features that help
clinical intervention. distinguish Blake’s pouch cyst from other entities within
the Dandy-Walker continuum.
Cerebellar hypoplasia and dysplasia have diverse etiologies,
including chromosomal abnormalities (e.g., trisomy 13 3.3.5. Posterior fossa arachnoid cysts
and 18), intracranial hemorrhage, intrauterine infections, Arachnoid cysts (AC) are intra-arachnoid lesions that
and prenatal exposure to substances such as anticonvulsant expand by secreting CSF. Approximately 25% of these
drugs, alcohol, or cocaine. The cerebellum may be globally or cysts occur in the posterior fossa. They are in the extra-
34
unilaterally affected. When cerebellar and pons hypoplasia axial space and exert a mass effect, altering the shape of
28
occur together, it is termed pontocerebellar hypoplasia, surrounding brain structures and often causing scalloping
which may also be associated with cerebral atrophy and along the adjacent calvarium (Figure 9). The cysts
delayed myelination. Nonetheless, in muscular dystrophies, consistently exhibit CSF signal intensity across all imaging
29
cerebellar cysts, dysplasia, and hypoplasia represent sequences. Although mostly sporadic, arachnoid cysts
35
predominant features of brain involvement. Previous studies have been associated with syndromes such as Chudley-
30
have indicated that the simple dysplasia group has better McCullough syndrome, acrocallosal syndrome, and
postnatal outcomes compared to the group with associated autosomal recessive primary ciliary dyskinesia. It remains
Volume 11 Issue 2 (2025) 66 doi: 10.36922/jctr.6240