Page 58 - JCTR-9-4
P. 58
274 Li et al. | Journal of Clinical and Translational Research 2023; 9(4): 272-281
2.5. Ethnical statements 3.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.5.1. Ethical approval Ki-67 protein expression levels were measured in 59 patients.
The number of Ki-67-positive cells in each patient ranged from
This study was performed in accordance with the principles of the 20% to 100%, with a median of 75%. Immunohistochemistry
Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee showed that 92.2% (59/64), 41.9% (26/62), and 67.2% (41/61)
of Clinical Oncology School of Fujian Medical University, Fujian patients were positive for Syn, CgA, and CD56, respectively.PD-
Cancer Hospital (Review Number K2022-208-01). L1 expression was positive in 17 (37.8%) patients.
2.5.2. Consent to participate 3.3. OS
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants The follow-up period ranged from 13 to 156 months, with a
included in the study. median of 33 months. The 3- and 5-year OS was 41.7% and 35.2%,
2.5.3. Consent to publish and 3- and 5-year PFS was 35.6% and 30.6%, respectively. The
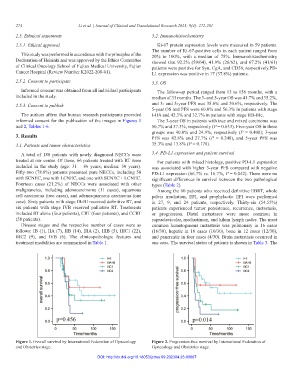
5-year OS and PFS were 60.0% and 56.3% in patients with stage
The authors affirm that human research participants provided I-IIA and 42.3% and 32.7% in patients with stage IIB-IIIc.
informed consent for the publication of the images in Figures 1 The 3-year OS in patients with true and mixed carcinoma was
and 2, Tables 1-6. 50.7% and 37.3%, respectively (P = 0.633). Five-year OS in these
groups was 40.0% and 24.9%, respectively (P = 0.400); 3-year
3. Results PFS was 42.8% and 27.7% (P = 0.248), and 5-year PFS was
3.1. Patients and tumor characteristics 35.3% and 13.8% (P = 0.178).
A total of 188 patients with newly diagnosed NECCs were 3.4. PD-L1 expression and patient survival
treated at our center. Of these, 66 patients treated with RT were For patients with mixed histology, positive PD-L1 expression
included in the study (age: 31 – 86 years; median: 50 years). was associated with higher 3-year PFS compared with negative
Fifty-two (78.8%) patients presented pure NECCs, including 50 PD-L1 expression (66.7% vs. 16.7%, P = 0.042). There were no
with SCNEC, one with LCNEC, and one with SCNEC + LCNEC. significant differences in survival between the two pathological
Fourteen cases (21.2%) of NECCs were associated with other types (Table 2).
malignancies, including adenocarcinoma (11 cases), squamous Among the 60 patients who received definitive EBRT, whole
cell carcinoma (two cases), and adenosquamous carcinoma (one pelvis irradiation, EFI, and prophylactic EFI were performed
case). Sixty patients with stage IB-III received definitive RT, and in 27, 9, and 24 patients, respectively. Thirty-six (54.55%)
six patients with stage IVB received palliative RT. Treatments patients experienced tumor persistence, recurrence, metastasis,
included RT alone (four patients), CRT (four patients), and CCRT or progression. Distal metastases were more common in
(58 patients). supraclavicular, mediastinum, and hilum lymph nodes. The most
Disease stages and the respective number of cases were as common hematogenous metastasis was pulmonary in 16 cases
follows: IB (1), IIA (7), IIB (14), IIIA (2), IIIB (5), IIIC1 (22), (16/30), hepatic in 10 cases (10/30), bone in 12 cases (12/30),
IIIC2 (9), and IVB (6). The clinicopathologic features and and pancreatic in four cases (4/30). Brain metastasis occurred in
treatment modalities are summarized in Table 1. one case. The survival status of patients is shown in Table 3. The
Figure 1. Overall survival by International Federation of Gynecology Figure 2. Progression-free survival by International Federation of
and Obstetrics stage. Gynecology and Obstetrics stage.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18053/jctres.09.202304.23-00067