Page 81 - MI-2-4
P. 81
Microbes & Immunity Dietary emulsifiers affect the presence of AIEC
A
B
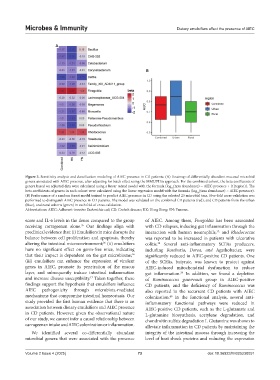
Figure 3. Sensitivity analysis and classification modeling of AIEC presence in CD patients. (A) Heatmap of differentially abundant mucosal microbial
genera associated with AIEC presence, after adjusting for batch effect using the MMUPHin approach. For the combined cohort, the beta coefficients of
genera based on adjusted data were calculated using a linear mixed model with the formula (log (taxa abundance) ~ AIEC presence + (1|region)). The
10
beta coefficients of genera in each cohort were calculated using the linear regression model with the formula (log (taxa abundance) ~ AIEC presence).
10
(B) Performance of a random forest model trained to predict AIEC presence in CD using the selected 23 microbial taxa. Five-fold cross-validation was
performed to distinguish AIEC presence in CD patients. The model was validated on the combined CD patients (red), and CD patients from the urban
(blue), and rural cohorts (green) in each fold of cross-validation.
Abbreviations: AIEC: Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli; CD: Crohn’s disease; HK: Hong Kong; YN: Yunnan.
score and IL-6 levels in the ileum compared to the group of AIEC. Among them, Finegoldia has been associated
receiving carrageenan alone. Our findings align with with CD relapses, inducing gut inflammation through the
35
preclinical evidence that: (i) Emulsifiers in mice disrupts the interaction with human neutrophils, and Rhodococcus
37,
balance between cell proliferation and apoptosis, thereby was reported to be increased in patients with ulcerative
altering the intestinal microenvironment; (ii) emulsifiers colitis. Several anti-inflammatory SCFAs producers,
36
38
have no significant effect on germ-free mice, indicating including Roseburia, Dorea, and Agathobacter, were
16
that their impact is dependent on the gut microbiome; significantly reduced in AIEC-positive CD patients. One
(iii) emulsifiers can enhance the expression of virulent of the SCFAs, butyrate, was known to protect against
genes in AIEC, promote its penetration of the mucus AIEC-induced mitochondrial dysfunction to reduce
layer, and subsequently induce intestinal inflammation gut inflammation. In addition, we found a depletion
39
and increase disease susceptibility. Taken together, these of Ruminococcus gauvreauii group in AIEC-positive
17
findings support the hypothesis that emulsifiers influence CD patients, and the deficiency of Ruminococcus was
AIEC pathogenicity through microbiota-mediated also reported in the recurrent CD patients with AIEC
mechanisms that compromise intestinal homeostasis. Our colonization. In the functional analysis, several anti-
40
study provided the first human evidence that there is an inflammatory functional pathways were reduced in
association between dietary emulsifiers and AIEC presence AIEC-positive CD patients, such as the L-glutamate and
in CD patients. However, given the observational nature L-glutamine biosynthesis, acetylene degradation, and
of our study, we cannot infer a causal relationship between chondroitin sulfate degradation I. Glutamine was shown to
carrageenan intake and AIEC colonization or inflammation. alleviate inflammation in CD patients by maintaining the
We identified several co-differentially abundant integrity of the intestinal mucosa through increasing the
microbial genera that were associated with the presence level of heat shock proteins and reducing the expression
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 73 doi: 10.36922/MI025230051