Page 82 - MI-2-4
P. 82
Microbes & Immunity Dietary emulsifiers affect the presence of AIEC
A
B
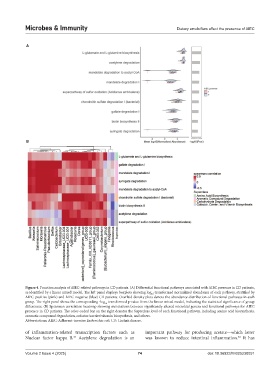
Figure 4. Function analysis of AIEC-related pathways in CD patients. (A) Differential functional pathways associated with AIEC presence in CD patients,
as identified by a linear mixed model. The left panel displays boxplots showing log -transformed normalized abundance of each pathway, stratified by
10
AIEC-positive (pink) and AIEC-negative (blue) CD patients. Overlaid density plots denote the abundance distribution of functional pathways in each
group. The right panel shows the corresponding -log transformed p-value from the linear mixed model, indicating the statistical significance of group
10
differences. (B) Spearman correlation heatmap showing associations between significantly altered microbial genera and functional pathways for AIEC
presence in CD patients. The color-coded bar on the right denotes the Superclass level of each functional pathway, including amino acid biosynthesis,
aromatic compound degradation, cofactor/carrier/vitamin biosynthesis, and others.
Abbreviations: AIEC: Adherent-invasive Escherichia coli; CD: Crohn’s disease.
of inflammation-related transcription factors such as important pathway for producing acetate—which latter
Nuclear factor kappa B. Acetylene degradation is an was known to reduce intestinal inflammation. It has
42
41
Volume 2 Issue 4 (2025) 74 doi: 10.36922/MI025230051