Page 120 - MSAM-2-3
P. 120
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing SLA 3D printed triaxial nozzle
A
B
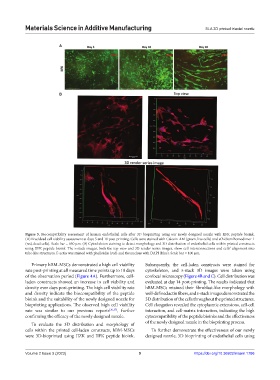
Figure 5. Biocompatibility assessment of human endothelial cells after 3D bioprinting using our newly designed nozzle with IIFK peptide bioink.
(A) Live/dead cell viability assessment at days 5 and 10 post-printing. Cells were stained with Calcein-AM (green, live cells) and ethidium homodimer-1
(red, dead cells). Scale bar = 650 μm. (B) Cytoskeleton staining to detect morphology and 3D distribution of endothelial cells within printed constructs
using IIFK peptide bioink. The z-stack images, both the top view and 3D render series images, show cell interconnections and cells’ alignment into
tube-like structures. F-actin was stained with phalloidin (red) and the nucleus with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 100 μm.
Primary hBM-MSCs demonstrated a high cell viability Subsequently, the cell-laden constructs were stained for
rate post-printing at all measured time points up to 10 days cytoskeleton, and z-stack 3D images were taken using
of the observation period (Figure 4A). Furthermore, cell- confocal microscopy (Figure 4B and C). Cell distribution was
laden constructs showed an increase in cell viability and evaluated at day 14 post-printing. The results indicated that
density over days post-printing. The high cell viability rate hBM-MSCs retained their fibroblast-like morphology with
and density indicate the biocompatibility of the peptide well-defined actin fibers, and z-stack images demonstrated the
bioink and the suitability of the newly designed nozzle for 3D distribution of the cells throughout the printed structures.
bioprinting applications. The observed high cell viability Cell elongation revealed the cytoplasmic extensions, cell-cell
rate was similar to our previous reports [36,37] , further interaction, and cell-matrix interaction, indicating the high
confirming the efficacy of the newly designed nozzle. cytocompatibility of the peptide bioinks and the effectiveness
To evaluate the 3D distribution and morphology of of the newly designed nozzle in the bioprinting process.
cells within the printed cell-laden constructs, hBM-MSCs To further demonstrate the effectiveness of our newly
were 3D-bioprinted using IIZK and IIFK peptide bioink. designed nozzle, 3D bioprinting of endothelial cells using
Volume 2 Issue 3 (2023) 9 https://doi.org/10.36922/msam.1786