Page 23 - MSAM-3-4
P. 23
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Additive manufacturing of active optics
layer-by-layer. SLS is widely used in the fabrication of multifunctional optical components with unprecedented
high-temperature, durable optical components, especially performance. These ongoing advancements highlight
110
those incorporating UCNPs for wavelength conversion the growing potential of SLS in cutting-edge applications,
applications. from photonics to optoelectronics, despite the challenges it
continues to overcome.
A notable application is the injection-seeded,
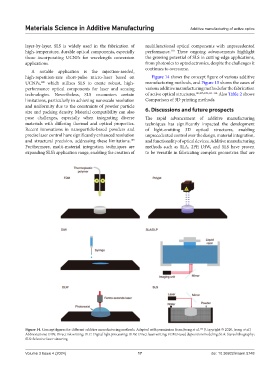
high-repetition-rate short-pulse micro-laser based on Figure 14 shows the concept figure of various additive
UCNPs, which utilizes SLS to create robust, high- manufacturing methods, and Figure 15 shows the cases of
108
performance optical components for laser and sensing various additive manufacturing methods for the fabrication
technologies. Nevertheless, SLS encounters certain of active optical structures. 40,105,108,111-114 Also Table 2 shows
limitations, particularly in achieving nanoscale resolution Comparison of 3D printing methods.
and uniformity due to the constraints of powder particle
size and packing density. Material compatibility can also 6. Discussions and future prospects
pose challenges, especially when integrating diverse The rapid advancement of additive manufacturing
materials with differing thermal and optical properties. techniques has significantly impacted the development
Recent innovations in nanoparticle‑based powders and of light-emitting 3D optical structures, enabling
precise laser control have significantly enhanced resolution unprecedented control over the design, material integration,
and structural precision, addressing these limitations. and functionality of optical devices. Additive manufacturing
109
Furthermore, multi-material integration techniques are methods such as SLA, 2PP, DIW, and SLS have proven
expanding SLS’s application range, enabling the creation of to be versatile in fabricating complex geometries that are
Figure 14. Concept figures for different additive manufacturing methods. Adapted with permission from Jeong et al. (Copyright © 2020, Jeong et al.)
111
Abbreviations: DIW: Direct ink writing; DLP: Digital light processing; DLW: Direct laser writing; FDM: Fused deposition modeling; SLA: Stereolithography;
SLS: Selective laser sintering
Volume 3 Issue 4 (2024) 17 doi: 10.36922/msam.5748