Page 107 - MSAM-4-1
P. 107
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Topology optimization of an aluminum bicycle pedal
crank using laser powder bed fusion
A
B
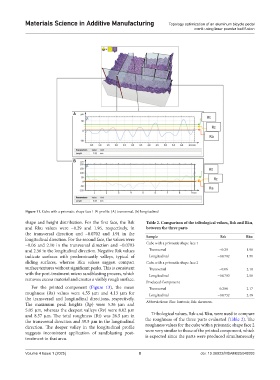
Figure 11. Cube with a prismatic shape face 1 W-profile: (A) transversal, (b) longitudinal
shape and height distribution. For the first face, the Rsk Table 2. Comparison of the tribological values, Rsk and Rku,
and Rku values were −0.29 and 1.96, respectively, in between the three parts
the transversal direction and −0.0702 and 1.91 in the Sample Rsk Rku
longitudinal direction. For the second face, the values were
−0.06 and 2.10 in the transversal direction and −0.0703 Cube with a prismatic shape face 1
and 2.56 in the longitudinal direction. Negative Rsk values Transversal −0.29 1.96
indicate surfaces with predominantly valleys, typical of Longitudinal −0.0702 1.91
sliding surfaces, whereas Rku values suggest compact Cube with a prismatic shape face 2
surface textures without significant peaks. This is consistent Transversal −0.06 2.10
with the post-treatment micro sandblasting process, which Longitudinal −0.0703 2.56
removes excess material and creates a visibly rough surface.
Produced Component
For the printed component (Figure 13), the mean Transversal 0.208 2.17
roughness (Ra) values were 4.55 µm and 4.13 µm for Longitudinal −0.0732 2.48
the transversal and longitudinal directions, respectively.
The maximum peak heights (Rp) were 5.36 µm and Abbreviations: Rku: kurtosis; Rsk: skewness.
5.05 µm, whereas the deepest valleys (Rv) were 8.02 µm
and 8.57 µm. The total roughness (Rt) was 26.5 µm in Tribological values, Rsk and Rku, were used to compare
the transversal direction and 39.5 µm in the longitudinal the roughness of the three parts evaluated (Table 2). The
direction. The deeper valley in the longitudinal profile roughness values for the cube with a prismatic shape face 2
suggests inconsistent application of sandblasting post- were very similar to those of the printed component, which
treatment in that area. is expected since the parts were produced simultaneously
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/MSAM025040003