Page 62 - MSAM-4-1
P. 62
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing In situ electromagnetic field manipulation during LMD
A B
D
C
E F
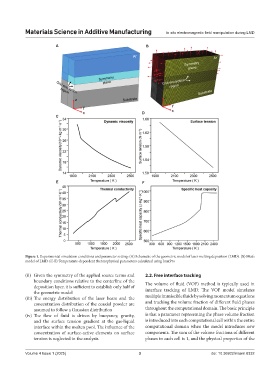
Figure 1. Experimental simulation conditions and parameter setting: (A) Schematic of the geometric model of laser melting deposition (LMD). (B) Mesh
model of LMD. (C-F) Temperature-dependent thermophysical parameters calculated using JmatPro
(ii) Given the symmetry of the applied source terms and 2.2. Free interface tracking
boundary conditions relative to the centerline of the The volume of fluid (VOF) method is typically used in
deposition layer, it is sufficient to establish only half of interface tracking of LMD. The VOF model simulates
the geometric model
(iii) The energy distribution of the laser beam and the multiple immiscible fluids by solving momentum equations
concentration distribution of the coaxial powder are and tracking the volume fraction of different fluid phases
assumed to follow a Gaussian distribution throughout the computational domain. The basic principle
(iv) The flow of fluid is driven by buoyancy, gravity, is that a parameter representing the phase volume fraction
and the surface tension gradient at the gas-liquid is introduced into each computational cell within the entire
interface within the molten pool. The influence of the computational domain when the model introduces new
concentration of surface-active elements on surface components. The sum of the volume fractions of different
tension is neglected in the analysis. phases in each cell is 1, and the physical properties of the
Volume 4 Issue 1 (2025) 3 doi: 10.36922/msam.8332