Page 67 - MSAM-4-3
P. 67
Materials Science in Additive Manufacturing Bead geometry prediction in laser-arc AM
A
B
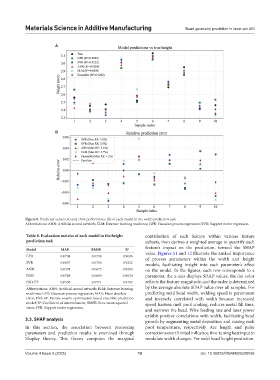
Figure 8. Predicted values (A) and error performance (B) of each model in the width prediction task
Abbreviations: ANN: Artificial neural network; ELM: Extreme learning machines; GPR: Gaussian process regression; SVR: Support vector regression
Table 8. Evaluation metrics of each model in the height contribution of each feature within various feature
prediction task subsets, then derives a weighted average to quantify each
feature’s impact on the prediction, termed the SHAP
Model MAE RMSE R 2
value. Figures 11 and 12 illustrate the ranked importance
GPR 0.0704 0.0798 0.9006 of process parameters within the width and height
SVR 0.0657 0.0706 0.9222 models, facilitating insight into each parameter’s effect
ANN 0.0591 0.0675 0.9289 on the model. In the figures, each row corresponds to a
ELM 0.0748 0.0869 0.8820 parameter, the x-axis displays SHAP values, the dot color
PSO-EP 0.0505 0.0571 0.9492 reflects the feature magnitude, and the order is determined
Abbreviations: ANN: Artificial neural network; ELM: Extreme learning by the average absolute SHAP value over all samples. For
machines; GPR: Gaussian process regression; MAE: Mean absolute predicting weld bead width, welding speed is paramount
error; PSO-EP: Particle swarm optimization-based ensemble prediction and inversely correlated with width because increased
model; R : Coefficient of determination; RMSE: Root mean squared speed hastens melt pool cooling, reduces metal fill time,
2
error; SVR: Support vector regression.
and narrows the bead. Wire feeding rate and laser power
exhibit positive correlations with width, facilitating bead
3.3. SHAP analysis growth by augmenting metal deposition and raising melt
In this section, the association between processing pool temperature, respectively. Arc length and pulse
parameters and prediction results is examined through corrections exert limited influence, fine-tuning heat input to
Shapley theory. This theory computes the marginal modulate width changes. For weld bead height prediction,
Volume 4 Issue 3 (2025) 10 doi: 10.36922/MSAM025220036