Page 46 - TD-3-1
P. 46
Tumor Discovery Energy metabolism in bladder cancer
A B
C
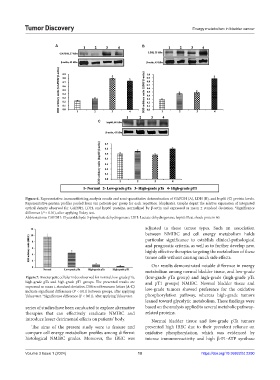
Figure 6. Representative immunoblotting analysis results and semi-quantitative determination of GAPDH (A), LDH (B), and hsp60 (C) protein levels.
Representative protein profiles pooled from ten patients per group for each repetition (duplicate). Graphs depict the relative expression of integrated
optical density observed for GAPDH, LDH, and hsp60 proteins, normalized by β-actin and expressed as mean ± standard deviation. *Significance
difference (P < 0.01), after applying Tukey test.
Abbreviations: GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LDH: Lactate dehydrogenase; hsp60: Heat shock protein 60.
adjusted to these tumor types. Such an association
between NMIBC and cell energy metabolism holds
particular significance to establish clinical-pathological
and prognostic criteria, as well as to further develop new,
highly effective therapies targeting the metabolism of these
tumor cells without causing much side effects.
Our results demonstrated notable difference in energy
metabolism among normal bladder tissue, and low-grade
Figure 7. Bioenergetic cellular index observed for normal, low-grade pTa, (low-grade pTa group) and high-grade (high-grade pTa
high-grade pTa and high-grade pT1 groups. The presented results are and pT1 groups) NMIBC. Normal bladder tissue and
expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Different lowercase letters (A‑C) low-grade tumors showed preference for the oxidative
indicate significant differences (P < 0.01) between groups, after applying
Tukey test. *Significance difference (P < 0.01), after applying Tukey test. phosphorylation pathway, whereas high-grade tumors
leaned toward glycolytic metabolism. These findings were
series of studies have been conducted to explore alternative based on the analysis applied to several metabolic pathway-
therapies that can effectively eradicate NMIBC and related proteins.
introduce lesser detrimental effects on patients’ body. Normal bladder tissue and low-grade pTa tumors
The aims of the present study were to feature and presented high IBEC due to their prevalent reliance on
compare cell energy metabolism profiles among different oxidative phosphorylation, which was evidenced by
histological NMIBC grades. Moreover, the IBEC was intense immunoreactivity and high β-F1-ATP synthase
Volume 3 Issue 1 (2024) 10 https://doi.org/10.36922/td.2290