Page 86 - TD-4-2
P. 86
Tumor Discovery DRGs in HCC prognosis and immunity
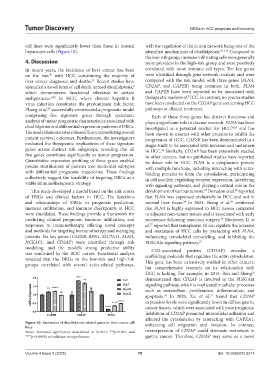
cell lines were significantly lower than those in normal with the regulation of the action network being one of the
hepatocyte cells (Figure 10). identified mechanisms of disulfidptosis. 8,13,16 Compared to
the low-risk group, immune infiltrating cells were generally
4. Discussion more prevalent in the high-risk group and were positively
In recent years, the incidence of liver cancer has been correlated with most immune cell types. Ten key genes
on the rise, with HCC constituting the majority of were identified through gene network analysis and were
20
liver cancer diagnoses and deaths. Recent studies have compared with the risk model, with three genes (FLNA,
21
identified a novel form of cell death termed disulfidptosis, CD2AP, and CAPZB) being common in both. FLNA
8
which demonstrates functional relevance in certain and CAPZB have been reported to be associated with
malignancies. In HCC, where chronic hepatitis B therapeutic markers of HCC. In contrast, no precise studies
8,22
virus infection constitutes the predominant risk factor, have been conducted on the CD2AP gene concerning HCC
Zhang et al. successfully constructed a prognostic model pathways or clinical treatment.
23
comprising five signature genes through systematic Each of these three genes has distinct functions and
analysis of tumor prognostic characteristics associated with plays a significant role in disease research. FLNA has been
disulfidptosis and differential expression patterns of DRGs. investigated as a potential marker for HCC 24,25 and has
The model demonstrates robust efficacy in predicting overall been shown to interact with other proteins to inhibit the
patient survival outcomes. Furthermore, the investigators progression of HCC. CAPZB has been demonstrated in a
evaluated the therapeutic implications of these signature single study to be associated with invasion and metastasis
genes across distinct risk subgroups, revealing that all in HCC. Similarly, CD2AP has been extensively studied
26
five genes contribute significantly to tumor progression. in other cancers, but no published studies have reported
Quantitative expression profiling of these genes enabled its direct role in HCC. FLNA is a cytoplasmic protein
precise stratification of patients into molecular subtypes with multiple functions, including interacting with actin-
with differential prognostic trajectories. These findings binding proteins to form the cytoskeleton, participating
collectively suggest the feasibility of targeting DRGs as a in cell motility, regulating receptor expression, interfering
viable immunotherapeutic strategy. with signaling pathways, and playing a critical role in the
28
27
This study developed a model based on the risk scores development of various tumors. Donadon et al. reported
of DRGs and clinical factors in HCC. The functions that FLNA was expressed exclusively in HCC and not in
and relationships of DRGs in prognosis prediction, normal liver tissue. In 2021, Sheng et al. confirmed
28
29
immune infiltration, and immune checkpoints in HCC that FLNA is highly expressed in HCC tissues compared
were elucidated. These findings provide a framework for to adjacent non-tumor tissues and is associated with early
predicting clinical prognosis, immune infiltration, and recurrence following resection surgery. Moreover, Li et
29
responses to immunotherapy, offering novel concepts al. reported that semaphorin 3d can regulate the invasion
27
and methods for targeting immunotherapy and managing and metastasis of HCC cells by interacting with FLNA,
patients. Six key genes (CAPZB, RPN1, SLC7A11, FLNA, influencing cytoskeletal remodeling, and inhibiting the
NCKAP1, and CD2AP) were identified through risk PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. 27
modeling, and the model’s strong predictive ability CD2-associated protein (CD2AP) encodes a
was confirmed by the ROC curves. Functional analysis scaffolding molecule that regulates the actin cytoskeleton.
revealed that the DRGs in the low-risk and high-risk This gene has been extensively studied in other cancers,
groups correlated with several actin-related pathways,
but comprehensive research on its relationship with
30
HCC is lacking. For example, in 2016, Ren and Sheng
demonstrated that CD2AP is involved in the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway, which is implicated in cellular processes
such as metabolism, proliferation, differentiation, and
apoptosis. In 2020, Xie et al. found that CD2AP
30
31
expression levels were significantly lower in diffuse gastric
cancer tissues, which were associated with poor prognosis.
Inhibition of CD2AP promoted intercellular adhesion and
affected the cytoskeleton by interacting with CAPZA1,
Figure 10. Expression of disulfidptosis-related genes in liver cancer cell enhancing cell migration and invasion. In contrast,
lines
Notes: Statistical significance determined at *p<0.01, ***p<0.001, and overexpression of CD2AP could attenuate metastasis in
****p<0.0001); ns indicates no significance. gastric cancer. Therefore, CD2AP may serve as a novel
Volume 4 Issue 2 (2025) 78 doi: 10.36922/td.8214