Page 64 - AJWEP-v22i3
P. 64
Almoshadak
other sites. Notably, the highest concentration of Co
(2.48 mg/g DM) was observed in the roots at site S2,
whereas the highest concentration of Ni (0.61 mg/g
DM) was found in the roots at site S3. A similar
pattern of metal accumulation in the roots at site S1
was also observed in the leaves of the same site, with
concentrations of Al, Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn being 0.35,
0.67, 0.17, 0.72, and 0.19 mg/g DM, respectively.
Leaves at site S2 accumulated a higher concentration
of Co (2.47 mg/g DM), whereas leaves at site S3
accumulated more Cr and Ni (0.12 and 1.24 mg/g DM,
respectively) compared to other sites. Notably, the
investigation revealed the remarkable phytoremediation
potential of S. monoica roots for Zn, Co, and Pb and the
leaves’ ability to remediate a substantial amount of Co,
Ni, and Cd despite their toxicity to the plant.
The observed differences in heavy metal
accumulation between sites may reflect variations in soil
metal concentrations, salinity, and plant metal uptake
efficiency. The higher accumulation of Zn and Pb in
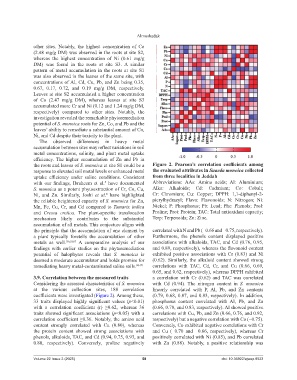
the roots and leaves of S. monoica at site S1 could be a Figure 2. Pearson’s correlation coefficients among
response to elevated soil metal levels or enhanced metal the evaluated attributes in Suaeda monoica collected
uptake efficiency under saline conditions. Consistent from three localities in Jeddah
with our findings, Ibraheem et al. have documented Abbreviations: AAs: Amino acids; Al: Aluminium;
5
S. monoica as a potent phytoextraction of Cr, Co, Cu, Alka: Alkaloids; Cd: Cadmium; Co: Cobalt;
Ni, and Zn. Similarly, Joshi et al. have highlighted Cr: Chromium; Cu: Copper; DPPH: 1,1-diphenyl-2-
8
the reliable heightened capacity of S. monoica for Zn, picrylhydrazyl; Flavo: Flavonoids; N: Nitrogen; Ni:
Mn, Fe, Cu, Cr, and Cd compared to Tamarix indica Nickel; P: Phosphorus; Pb: Lead; Phe: Phenols; Prol:
and Cressa cretica. The plant-specific translocation Proline; Prot: Protein; TAC: Total antioxidant capacity;
mechanism likely contributes to the substantial Terp: Terpenoids; Zn: Zinc.
accumulation of all metals. This conjecture aligns with
the principle that the accumulation of one element by correlated with N and Pb (−0.66 and −0.75, respectively).
a plant typically foretells the accumulation of other Furthermore, the phenols content displayed positive
metals as well. 59,60,67 A comparative analysis of our associations with alkaloids, TAC, and Cd (0.76, 0.95,
findings with earlier studies on the phytoremediation and 0.89, respectively), whereas the flavonoid content
potential of halophytes reveals that S. monoica is exhibited positive associations with Cr (0.83) and Ni
deemed a moderate accumulator and holds promise for (0.62). Similarly, the alkaloid content showed strong
remediating heavy metal-contaminated saline soils. 68-70 correlations with TAC, Cd, Cr, and Cu (0.66, 0.69,
0.65, and 0.62, respectively), whereas DPPH exhibited
3.9. Correlation between the measured traits a correlation with Cr (0.62) and TAC was correlated
Considering the assessed characteristics of S. monoica with Cd (0.94). The nitrogen content in S. monoica
at the various collection sites, 188 correlation linearly correlated with P, Al, Pb, and Zn contents
coefficients were investigated (Figure 2). Among these, (0.79, 0.68, 0.87, and 0.83, respectively). In addition,
33 traits displayed highly significant values (p<0.01) phosphorus content correlated with Al, Pb, and Zn
with a correlation coefficient (r) ≥0.62, whereas 36 (0.66, 0.70, and 0.83, respectively). Al showed positive
traits showed significant associations (p<0.05) with a correlations with Cu, Pb, and Zn (0.66, 0.76, and 0.92,
correlation coefficient ≥0.36. Notably, the amino acid respectively) but a negative correlation with Co (−0.75).
content strongly correlated with Cu (0.80), whereas Conversely, Co exhibited negative correlations with Cr
the protein content showed strong associations with and Cu (−0.70 and −0.66, respectively), whereas Cr
phenols, alkaloids, TAC, and Cd (0.94, 0.75, 0.93, and positively correlated with Ni (0.85), and Pb correlated
0.80, respectively). Conversely, proline negatively with Zn (0.88). Notably, a positive relationship was
Volume 22 Issue 3 (2025) 58 doi: 10.36922/ajwep.8523