Page 59 - DP-1-1
P. 59
Design+ Approximate signed multipliers design approach
Specifically, the results indicate that the proposed
multiplier improves delay by at least 13%, reduces power
consumption by 12%, and decreases area by 9%, resulting
in a 9% improvement in the power-delay product compared
to the other designs.
4.2. Accuracy analysis
The accuracy analysis involves calculating metrics such as
the normalized mean error distance (NMED) and mean
relative error distance (MRED) to evaluate performance.
In addition, the number of effective bits (NoEB) is used to
measure error-free output bits, as these metrics provide a
more suitable comparison between different architectures
than basic metrics such as error rate and error distance. 36
Although NMED and MRED provide a general
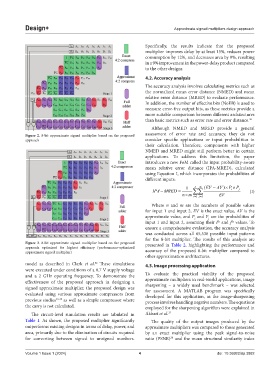
Figure 2. 8-bit approximate signed multiplier based on the proposed assessment of error rate and accuracy, they do not
approach consider specific applications or input probabilities in
their calculation. Therefore, components with higher
NMED and MRED might still perform better in certain
applications. To address this limitation, the paper
introduces a new FoM called the input probability-aware
mean relative error distance (IPA-MRED), calculated
using Equation I, which incorporates the probabilities of
different inputs:
1 n m (EV − AV ) P P× ×
IPA MRED− = ∑∑ i j (I)
n m× i= 1 j= 1 EV
Where n and m are the numbers of possible values
for input 1 and input 2, EV is the exact value, AV is the
approximate value, and P and P are the probabilities of
i
j
th
input 1 and input 2, assuming their i and j values. To
th
ensure a comprehensive evaluation, the accuracy analysis
was conducted across all 65,536 possible input patterns
for the 8-bit multiplier. The results of this analysis are
Figure 3. 8-bit approximate signed multiplier based on the proposed presented in Table 2, highlighting the performance and
approach optimized for highest efficiency (performance-optimized
approximate signed multiplier) accuracy of the proposed 8-bit multiplier compared to
other approximation architectures.
model as described in Clark et al. These simulations 4.3. Image processing application
32
were executed under conditions of a 0.7 V supply voltage
and a 2 GHz operating frequency. To demonstrate the To evaluate the practical viability of the proposed
effectiveness of the proposed approach in designing a approximate multipliers in real-world applications, image
signed approximate multiplier, the proposed design was sharpening – a widely used benchmark – was selected
for assessment. A MATLAB program was specifically
evaluated using various approximate compressors from developed for this application, as the image-sharpening
previous studies 33-35 as well as a simple compressor where process involves handling negative numbers. The equations
the carry is not calculated. employed for the sharpening algorithm were explained in
The circuit-level simulation results are tabulated in Akbari et al. 37
Table 1. As shown, the proposed multiplier significantly The quality of the output images produced by the
outperforms existing designs in terms of delay, power, and approximate multipliers was compared to those generated
area, primarily due to the elimination of circuits required by an exact multiplier using the peak signal-to-noise
for converting between signed to unsigned numbers. ratio (PSNR) and the mean structural similarity index
38
Volume 1 Issue 1 (2024) 4 doi: 10.36922/dp.3882