Page 67 - ESAM-1-4
P. 67
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing EST manipulates structure of Ti-6Al-4V/Cu
A B
C D
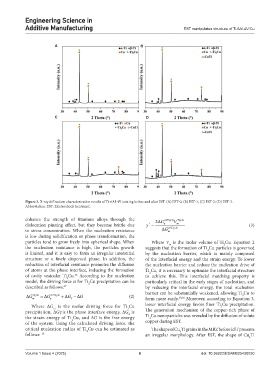
Figure 3. X-ray diffraction characterization results of Ti-6Al-4V coating before and after EST. (A) EST-0; (B) EST-1; (C) EST-2; (D) EST-3.
Abbreviation: EST: Electroshock treatment.
enhance the strength of titanium alloys through the 2G /Ti Cu V Ti 2 Cu
2
dislocation pinning effect, but they become brittle due m (3)
*
2
to stress concentration. When the nucleation resistance G /Ti Cu
m
is low during solidification or phase transformation, the
particles tend to grow freely into spherical shape. When Where V is the molar volume of Ti Cu. Equation 2
2
m
the nucleation resistance is high, the particles growth suggests that the formation of Ti Cu particles is governed
2
is limited, and it is easy to form an irregular interstitial by the nucleation barrier, which is mainly composed
structure or a finely dispersed phase. In addition, the of the interfacial energy and the strain energy. To lower
reduction of interfacial resistance promotes the diffusion the nucleation barrier and reduce the nucleation drive of
of atoms at the phase interface, inducing the formation Ti Cu, it is necessary to optimize the interfacial structure
2
of cavity vesicular Ti Cu. According to the nucleation to achieve this. This interfacial matching property is
36
2
model, the driving force α for Ti Cu precipitation can be particularly critical in the early stages of nucleation, and
2
described as follows: 37 by reducing the interfacial energy, the total nucleation
barrier can be substantially weakened, allowing Ti Cu to
G Ti Cu G / Ti Cu G G (2) form more easily. 33,36 Moreover, according to Equation 3,
2
2
2
m
S
Where ∆G is the molar driving force for Ti Cu lower interfacial energy favors finer Ti Cu precipitation.
2
m
2
precipitation, ∆G is the phase interface energy, ∆G is The generation mechanism of the copper-rich phase of
S
the strain energy of Ti Cu, and ∆G is the free energy Ti Cu nanoparticles was revealed by the diffusion of solute
2
2
of the system. Using the calculated driving force, the copper during EST.
critical nucleation radius of Ti Cu can be estimated as The shape of Cu Ti grains in the MBZ before EST presents
2
4
follows: 38 an irregular morphology. After EST, the shape of Cu Ti
4
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2025) 6 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025430030