Page 69 - ESAM-1-4
P. 69
Engineering Science in
Additive Manufacturing EST manipulates structure of Ti-6Al-4V/Cu
A B C
D E F
G H I
J K L
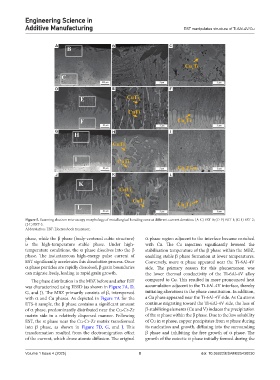
Figure 5. Scanning electron microscopy morphology of metallurgical bonding zone at different current densities. (A-C) EST-0; (D-F) EST-1; (G-I) EST-2;
(J-L) EST-3.
Abbreviation: EST: Electroshock treatment.
phase, while the β phase (body-centered cubic structure) α phase region adjacent to the interface became enriched
is the high-temperature stable phase. Under high- with Cu. The Cu injection significantly lowered the
temperature conditions, the α phase dissolves into the β stabilization temperature of the β phase within the MBZ,
phase. The instantaneous high-energy pulse current of enabling stable β phase formation at lower temperatures.
EST significantly accelerates this dissolution process. Once Conversely, more α phase appeared near the Ti-6Al-4V
α phase particles are rapidly dissolved, β grain boundaries side. The primary reason for this phenomenon was
can migrate freely, leading to rapid grain growth. the lower thermal conductivity of the Ti-6Al-4V alloy
The phase distribution in the MBZ before and after EST compared to Cu. This resulted in more pronounced heat
was characterized using EBSD (as shown in Figure 7A, D, accumulation adjacent to the Ti-6Al-4V interface, thereby
G, and J). The MBZ primarily consists of β, interspersed initiating alterations in the phase constitution. In addition,
with α and Cu phases. As depicted in Figure 7A for the a Cu phase appeared near the Ti-6Al-4V side. As Cu atoms
ETS-0 sample, the β phase contains a significant amount continue migrating toward the Ti-6Al-4V side, the loss of
of α phase, predominantly distributed near the Cu-Cr-Zr β-stabilizing elements (Cu and V) induces the precipitation
matrix side in a relatively dispersed manner. Following of the α phase within the β phase. Due to the low solubility
EST, the α phase near the Cu-Cr-Zr matrix transformed of Cu in α phase, copper precipitates from α phase during
into β phase, as shown in Figure 7D, G, and J. This its nucleation and growth, diffusing into the surrounding
transformation resulted from the electromigration effect β phase and inhibiting the free growth of α phase. The
of the current, which drove atomic diffusion. The original growth of the eutectic α phase initially formed during the
Volume 1 Issue 4 (2025) 8 doi: 10.36922/ESAM025430030