Page 88 - GPD-2-1
P. 88
Gene & Protein in Disease A pan-cancer analysis of HMGB1
A
C
B
D
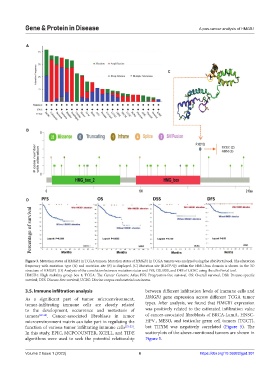
Figure 3. Mutation status of HMGB1 in TCGA tumors. Mutation status of HMGB1 in TCGA tumors was analyzed using the cBioPortal tool. The alteration
frequency with mutation type (A) and mutation site (B) is displayed. (C) Mutation site (R163*/Q) within the HMG-box domain is shown in the 3D
structure of HMGB1. (D) Analysis of the correlation between mutation status and PFS, OS, DSS, and DFS of UCEC using the cBioPortal tool.
HMGB1: High mobility group box 1; TCGA: The Cancer Genome Atlas; PFS: Progression-free survival, OS: Overall survival, DSS: Disease-specific
survival; DFS: Disease-free survival; UCEC: Uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma.
3.5. Immune infiltration analysis between different infiltration levels of immune cells and
As a significant part of tumor microenvironment, HMGB1 gene expression across different TCGA tumor
tumor-infiltrating immune cells are closely related types. After analysis, we found that HMGB1 expression
to the development, occurrence and metastasis of was positively related to the estimated infiltration value
tumors [18-20] . Cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumor of cancer-associated fibroblasts of BRCA-LumA, HNSC-
-
microenvironment matrix can take part in regulating the HPV , MESO, and testicular germ cell tumors (TGCT),
function of various tumor infiltrating immune cells [21-23] . but THYM was negatively correlated (Figure 5). The
In this study, EPIC, MCPCOUNTER, XCELL, and TIDE scatterplots of the above-mentioned tumors are shown in
algorithms were used to seek the potential relationship Figure 5.
Volume 2 Issue 1 (2023) 6 https://doi.org/10.36922/gpd.301