Page 93 - IJAMD-1-3
P. 93
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Review of gas turbine blade failures by erosion
erosion-induced material weakening. The detachment fractured blades. Corrosion and erosion emerged as
of the blade from the aerofoil is a serious issue that the predominant failure mechanisms, as deduced from
compromises the turbine’s functionality and can lead their comprehensive analysis. Through meticulous
to catastrophic failure if undetected during operation. investigation, they concluded that the initial failure
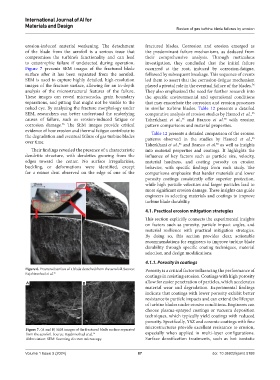
Figure 7 presents SEM images of the fractured blade occurred at the root, induced by corrosion-fatigue,
surface after it has been separated from the aerofoil. followed by subsequent breakage. This sequence of events
SEM is used to capture highly detailed, high-resolution led them to assert that the corrosion-fatigue mechanism
images of the fracture surface, allowing for an in-depth played a pivotal role in the eventual failure of the blades.
76
analysis of the microstructural features of the failure. They also emphasized the need for further research into
These images can reveal microcracks, grain boundary the specific environmental and operational conditions
separations, and pitting that might not be visible to the that may exacerbate the corrosion and erosion processes
naked eye. By analyzing the fracture morphology under in similar turbine blades. Table 12 presents a detailed
SEM, researchers can better understand the underlying comparative analysis of erosion studies by Hamed et al.,
55
causes of failure, such as erosion-induced fatigue or Taherkhani et al., and Branco et al. with erosion
56
58
corrosion damage. The SEM images provide critical pattern comparisons and material properties.
76
evidence of how erosion and thermal fatigue contribute to Table 12 presents a detailed comparison of the erosion
the degradation and eventual failure of gas turbine blades patterns observed in the studies by Hamed et al.,
55
over time.
Taherkhani et al., and Branco et al. as well as insights
56
58
Their findings revealed the presence of a characteristic into material properties and coatings. It highlights the
dendritic structure, with dendrites growing from the influence of key factors such as particle size, velocity,
edges toward the center. No surface irregularities, material hardness, and coating porosity on erosion
buckling, or deformations were identified, except behavior, with specific findings from each study. The
for a minor dent observed on the edge of one of the comparisons emphasize that harder materials and lower
porosity coatings consistently offer superior protection,
while high particle velocities and larger particles lead to
more significant erosion damage. These insights can guide
engineers in selecting materials and coatings to improve
turbine blade durability.
4.1. Practical erosion mitigation strategies
This section explicitly connects the experimental insights
on factors such as porosity, particle impact angles, and
material resilience with practical mitigation strategies.
By doing so, this section provides clear, actionable
recommendations for engineers to improve turbine blade
durability through specific coating techniques, material
selection, and design modifications.
4.1.1. Porosity in coatings
Figure 6. Fractured surface of a blade detached from the aerofoil. Source: Porosity is a critical factor influencing the performance of
Rajabinezhad et al. 76
coatings in resisting erosion. Coatings with high porosity
A B allow for easier penetration of particles, which accelerates
material wear and degradation. Experimental findings
indicate that coatings with lower porosity exhibit better
resistance to particle impacts and can extend the lifespan
of turbine blades under erosive conditions. Engineers can
choose plasma-sprayed coatings or vacuum deposition
techniques, which typically yield coatings with reduced
porosity. Specifically, YSZ and ceramic coatings with fine
microstructures provide excellent resistance to erosion,
Figure 7. (A and B) SEM images of the fractured blade surface separated
from the aerofoil. Source: Rajabinezhad et al. 76 especially when applied in multi-layer configurations.
Abbreviation: SEM: Scanning electron microscopy. Surface densification treatments, such as hot isostatic
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 87 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.5188