Page 94 - IJAMD-1-3
P. 94
International Journal of AI for
Materials and Design
Review of gas turbine blade failures by erosion
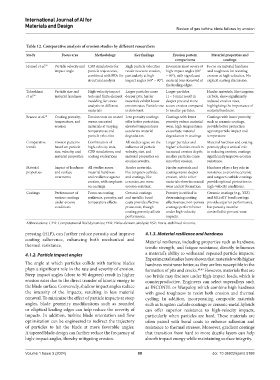
Table 12. Comparative analysis of erosion studies by different researchers
Study Focus area Methodology Key findings Erosion pattern Material properties and
comparisons coatings
Hamed et al. 55 Particle velocity and CFD simulations for High particle velocities Erosion is most severe at Focus on material hardness
impact angle particle trajectories, result in severe erosion, high impact angles (60° and toughness for resisting
combined with FEA for particularly at high – 90°), with significant erosion at high velocities. No
structural analysis impact angles (60° – 90°). material loss observed at explicit coating discussion.
the leading edges.
Taherkhani Particle size and High-velocity impact Larger particles cause Larger particles Harder materials, like tungsten
et al. 56 material hardness tests and finite element deeper pits; harder (1 – 5 mm) result in carbide, show significantly
modeling for stress materials exhibit lower deeper pits and more reduced erosion rates,
analysis on different erosion rates. Particle size severe erosion compared highlighting the importance of
materials is dominant. to smaller particles. material hardness.
Branco et al. 58 Coating porosity, Erosion tests on coated Low porosity coatings Coatings with lower Coatings with lower porosity,
temperature, and versus uncoated offer better protection; porosity reduce material such as ceramic coatings,
erosion materials at varying elevated temperatures wear; high temperatures provide better protection
temperatures and accelerate material exacerbate material against particle impact and
particle velocities degradation. degradation in coatings. temperature.
Comparative Erosion patterns Combination of All studies agree on the Larger particles and Material hardness and coating
trends based on particle high-velocity tests, influence of particle higher velocities result in porosity play a critical role
size, velocity, and CFD simulations, and velocity, size, and increased erosion depth; in reducing erosion; coatings
material properties coating evaluations material properties on smaller particles cause significantly improve erosion
erosion severity. smoother erosion. resistance.
Material Impact of hardness All studies assess Harder materials, Harder materials and Hardness plays a key role in
properties and surface material hardness like tungsten carbide, coatings resist deeper resistance to erosion; ceramic
treatments and resilience against and coatings, like erosion, while softer and tungsten carbide coatings
erosion, with emphasis ceramics, are more materials show increased provide optimal protection in
on coatings. erosion-resistant. wear and pit formation. high-velocity conditions.
Coatings Performance of Focus on coating Ceramic coatings Porosity is critical in Ceramic coatings (e.g., YSZ)
various coatings resilience, porosity, and and metallic bond determining coating and MCrAlY bond coatings
under erosive temperature effects coats provide effective effectiveness; non-porous provide superior performance,
conditions protection, though coatings perform better but porosity must be
coating porosity affects under high-velocity controlled to prevent wear.
performance. impacts.
Abbreviations: CFD: Computational fluid dynamics; FEA: Finite element analysis; YSZ: Yttria-stabilized zirconia.
pressing (HIP), can further reduce porosity and improve 4.1.3. Material resilience and hardness
coating adherence, enhancing both mechanical and Material resilience, including properties such as hardness,
thermal resistance. tensile strength, and fatigue resistance, directly influences
4.1.2. Particle impact angles a material’s ability to withstand repeated particle impacts.
Experimental studies have shown that materials with higher
The angle at which particles collide with turbine blades hardness resist wear better, as they are less susceptible to the
plays a significant role in the rate and severity of erosion. formation of pits and cracks. 48,49 However, materials that are
Steep impact angles (close to 90 degrees) result in higher too brittle may fracture under high-impact loads, which is
erosion rates due to the direct transfer of kinetic energy to counterproductive. Engineers can select superalloys such
the blade surface. Conversely, shallow impact angles reduce as INCONEL or Waspaloy, which combine high hardness
the intensity of the impacts, resulting in less material with good toughness to resist both erosion and thermal
removal. To minimize the effect of particle impacts at steep cycling. In addition, incorporating composite materials
angles, blade geometry modifications such as rounded such as tungsten carbide coatings or ceramic-metal hybrids
or elliptical leading edges can help reduce the severity of can offer superior resistance to high-velocity impacts,
impacts. In addition, turbine blade orientation and flow particularly when particles are hard. These materials are
optimization can be engineered to redirect the trajectory often paired with bond coats to enhance adhesion and
of particles to hit the blade at more favorable angles. resistance to thermal stresses. Moreover, gradient coatings
A tapered blade design can further reduce the frequency of that transition from hard to more ductile layers can help
high-impact angles, thereby mitigating erosion. absorb impact energy while maintaining surface integrity.
Volume 1 Issue 3 (2024) 88 doi: 10.36922/ijamd.5188