Page 292 - IJB-10-1
P. 292
International Journal of Bioprinting Scaffolds manufacturing by fused deposition modeling
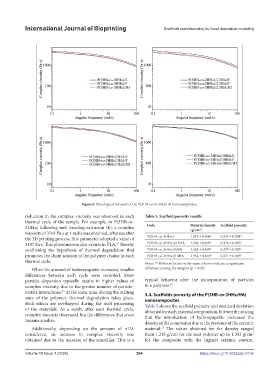
Figure 6. Rheological behavior of the P(3HB-co-3HHx)/HA nanocomposites.
reduction in the complex viscosity was observed in each Table 5. Scaffold porosity results
thermal cycle of the sample. For example, in P(3HB-co-
3HHx) following melt bending extrusion (E), a complex Code Material density Scaffold porosity
(g/cm )
3
viscosity of 3761 Pa·s at 1 rad/s was obtained, whereas after a a
the 3D printing process, this parameter adopted a value of P(3HB-co-3HHx) 1.215 ± 0.008 0.378 ± 0.004
3197 Pa·s. This phenomenon also occurs in PLA, thereby P(3HB-co-3HHx)/2.5HA 1.254 ± 0.007 a 0.376 ± 0.005 a
82
confirming the hypothesis of thermal degradation that P(3HB-co-3HHx)/5HA 1.263 ± 0.007 a 0.373 ± 0.003 a
promotes the chain scission of the polymer chains in each P(3HB-co-3HHx)/10HA 1.352 ± 0.010 b 0.371 ± 0.005 a
thermal cycle. Notes: Different letters in the same column indicate a significant
a,b
When the amount of hydroxyapatite increased, smaller difference among the samples (p < 0.05).
differences between each cycle were recorded. More
particle dispersion typically results in higher values of typical behavior after the incorporation of particles
complex viscosity, due to the greater number of particle- in a polymer. 84
matrix interactions. At the same time, during the melting 3.4. Scaffolds porosity of the P(3HB-co-3HHx/HA)
83
state of the polymer, thermal degradation takes place. nanocomposites
Both effects are overlapped during the melt processing Table 5 shows the scaffold porosity and standard deviation
of the materials. As a result, after each thermal cycle, obtained for each material composition. It is worth noticing
complex viscosity decreased, but the differences that arose that the introduction of hydroxyapatite increased the
became smaller.
density of the composites due to the presence of the ceramic
Additionally, depending on the amount of nHA material. The values obtained for the density ranged
25
considered, an increase in complex viscosity was from 1.215 g/cm for the neat polymer up to 1.352 g/cm
3
3
obtained due to the increase of the nanofiller. This is a for the composite with the highest ceramic content.
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 284 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0156