Page 293 - IJB-10-1
P. 293
International Journal of Bioprinting Scaffolds manufacturing by fused deposition modeling
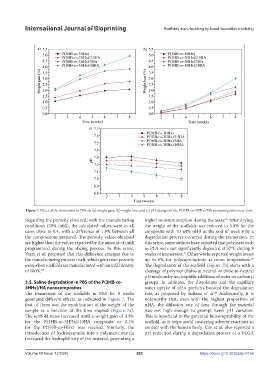
Figure 7. Effect of the immersion in PBS on (a) weight gain, (b) weight loss, and (c) pH changes of the P(3HB-co-3HHx)/HA nanocomposites over time.
Regarding the porosity obtained, with the manufacturing higher moisture sorption during the assay. After drying,
86
conditions (70% infill), the calculated values were in all the weight of the scaffolds was reduced to 3.0% for the
cases close to 0.4, with a difference of 1.9% between all composite with 10 wt% nHA at the end of week 8 by a
the compositions prepared. The porosity values obtained degradation process occurred during the immersion. In
are higher than the values expected by the amount of infill this sense, some authors have reported that polymers such
programmed during the slicing process. In this sense, as PLA were not significantly degraded at 37°C during 8
Vaezi et al. proposed that this difference emerges due to weeks of immersion. Other works reported weight losses
87
the manufacturing process itself, which generates porosity up to 6% for polycaprolactone at room temperature.
30
even when scaffolds are manufactured with an infill density The degradation of the scaffold (Figure 7b) starts with a
of 100%. 85 cleavage of polymer chains at neutral or close-to-neutral
pH medium by nucleophilic additions of water on carbonyl
3.5. Saline degradation in PBS of the P(3HB-co- groups. In addition, the dissolution and the capillary
3HHx)/HA nanocomposites water uptake of nHA particles boosted the degradation
The immersion of the scaffolds in PBS for 8 weeks rate, as proposed by Sultana et al. Additionally, it is
88
generated different effects, as indicated in Figure 7. The noteworthy that, even with the highest proportion of
first of them was the modification of the weight of the nHA, the diffusion rate of ions through the material
sample as a function of the time elapsed (Figure 7a). was not high enough to prompt harsh pH variation.
The scaffold mass increased until a weight gain of 4.9% This is beneficial to the potential biocompatibility of the
for the P(3HB-co-3HHx)/10HA composite or 2.1% scaffold, as it helps avoid catalyzing adverse reactions in
for the P(3HB-co-HHx) was reached. Similarly, the contact with the human body. Kim et al. also reported a
introduction of hydroxyapatite into a polymeric matrix pH reduction during a degradation process of a PLGA
increased the hydrophilicity of the material, promoting a
Volume 10 Issue 1 (2024) 285 https://doi.org/10.36922/ijb.0156