Page 58 - IJB-2-2
P. 58
Rheological study on 3D printability of alginate hydrogel and effect of graphene oxide
(a) (b) 0.35
0.6 Alg10 Alg10
GO0.05/Alg10 GO0.05/Alg10
GO0.15/Alg10 GO0.15/Alg10
GO0.25/Alg10 0.30 GO0.25/Alg10
0.5
Width (cm) 0.4 Height (cm) 0.25
0.3 0.20
0.2 0.15
0 5 10 15 20 0 5 10 15 20
Time (min) Time (min)
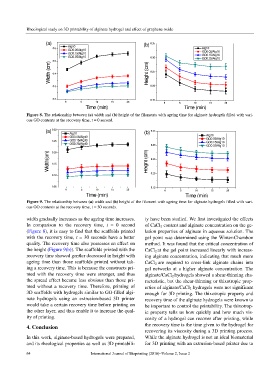
Figure 8. The relationship between (a) width and (b) height of the filaments with ageing time for alginate hydrogels filled with vari-
ous GO contents at the recovery time, t = 0 second.
(a) 0.30 (b) 0.35
Alg10
GO0.05/Alg10 Alg10
GO0.05/Alg10
0.25 GO0.15/Alg10 GO0.15/Alg10
GO0.25/Alg10 0.30 GO0.25/Alg10
0.20
Width(cm) 0.15 Height (cm) 0.25
0.10 0.20
0.05 0.15
0 5 10 15 20 0 5 10 15 20
Time (min) Time (min)
Figure 9. The relationship between (a) width and (b) height of the filament with ageing time for alginate hydrogels filled with vari-
ous GO contents at the recovery time, t = 30 seconds.
width gradually increases as the ageing time increases. ty have been studied. We first investigated the effects
In comparison to the recovery time, t = 0 second of CaCl 2 content and alginate concentration on the ge-
(Figure 8), it is easy to find that the scaffolds printed lation properties of alginate in aqueous solution. The
with the recovery time, t = 30 seconds have a better gel point was determined using the Winter-Chambon
quality. The recovery time also possesses an effect on method. It was found that the critical concentration of
the height (Figure 9(b)). The scaffolds printed with the CaCl 2 at the gel point increased linearly with increas-
recovery time showed gentler decreased in height with ing alginate concentration, indicating that much more
ageing time than those scaffolds printed without tak- CaCl 2 are required to cross-link alginate chains into
ing a recovery time. This is because the constructs pri- gel networks at a higher alginate concentration. The
nted with the recovery time were stronger, and thus alginate/CaCl 2 hydrogels showed a shear-thinning cha-
the spread effect became less obvious than those pri- racteristic, but the shear-thinning or thixotropic prop-
nted without a recovery time. Therefore, printing of erties of alginate/CaCl 2 hydrogels were not significant
3D scaffolds with hydrogels similar to GO-filled algi- enough for 3D printing. The thixotropic property and
nate hydrogels using an extrusion-based 3D printer recovery time of the alginate hydrogels were known to
would take a certain recovery time before printing on be important to control the printability. The thixotrop-
the other layer, and thus enable it to increase the qual- ic property tells us how quickly and how much vis-
ity of printing. cosity of a hydrogel can recover after printing, while
4. Conclusion the recovery time is the time given to the hydrogel for
recovering its viscosity during a 3D printing process.
In this work, alginate-based hydrogels were prepared, While the alginate hydrogel is not an ideal biomaterial
and its rheological properties as well as 3D printabili- for 3D printing with an extrusion-based printer due to
64 International Journal of Bioprinting (2016)–Volume 2, Issue 2