Page 56 - IJB-2-2
P. 56
Rheological study on 3D printability of alginate hydrogel and effect of graphene oxide
material maybe quickly decrease when being printed recover more significantly with longer recovery time.
and it needs a period of time to recover its viscosity. After that, we found that the quality of printing was
We here define the recovery time as the duration from obviously improved, as proved by comparing the im-
the finishing time of a current layer printed until the ages of the printed scaffolds shown in Figure 7(b).
printer starts to print and deposit a new layer on the Figures 7(c) and (d) show the effect of GO content
current layer. Therefore, it would be necessary to find on the width and height of filaments at the recovery
a reasonable recovery time that can improve the qual- time, t = 0 and t = 30 seconds, respectively. It can be
ity of printing. Based on the previous discussion in seen that the width of filament with the recovery time,
Section 3.2, a recovery time of 30 seconds was set as t = 0 is bigger than that at the recovery time, t = 30
the extruded hydrogels would recover most of its vis- seconds. This is because that most of the hydrogel’s
cosity after 30 seconds, and the viscosity could not viscosity already recovered after 30 seconds of rest,
Figure 5. The images of printed hydrogel scaffolds at different ageing times. (a) 0.5 minutes; (b) 5 minutes; (c) 10 minutes; (d) 15
minutes; (e) 20 minutes; (f) the effect of ageing time on filament width for 2 wt.% alginate hydrogels added with a fixed CaCl 2 con-
tent of 25 mM/L.
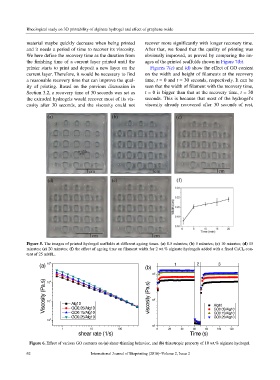
(a) 10 3 (b) 1 2 3
10 3
Viscosity (Pa.s) 10 1 Alg10 viscosity (Pa.s) 10 2 Alg10
2
10
GO0.05/Alg10
GO0.15/Alg10
GO0.15/Alg10
GO0.25/Alg10 GO0.05/Alg10
GO0.25/Alg10
10 0
10 1
1 10 100 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
shear rate (1/s) Time (s)
Figure 6. Effect of various GO contents on (a) shear-thinning behavior, and (b) thixotropic property of 10 wt.% alginate hydrogel.
62 International Journal of Bioprinting (2016)–Volume 2, Issue 2