Page 470 - IJB-10-2
P. 470
International Journal of Bioprinting Bioprinting with ASCs and bioactive glass
and averaged for known quantity of gelatin concentration 3. Results and discussion
to obtain a gelatin standard curve as shown in Figure 2b.
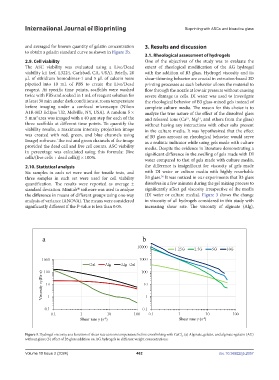
3.1. Rheological assessment of hydrogels
2.9. Cell viability One of the objectives of the study was to evaluate the
The ASC viability was evaluated using a Live/Dead extent of rheological modification of the AG hydrogel
viability kit (ref. L3224, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Briefly, 20 with the addition of B3 glass. Hydrogel viscosity and its
µL of ethidium homodimer-1 and 5 µL of calcein were shear-thinning behavior are crucial in extrusion-based 3D
pipetted into 10 mL of PBS to create the Live/Dead printing processes as such behavior allows the material to
reagent. At specific time points, scaffolds were washed flow through the nozzle at low air pressure without causing
twice with PBS and soaked in 1 mL of reagent solution for severe damage to cells. DI water was used to investigate
at least 30 min under dark conditions at room temperature the rheological behavior of B3 glass-mixed gels instead of
before imaging under a confocal microscope (Nikon complete culture media. The reason for this choice is to
A1R-HD Eclipse Ti2, Melville, NY, USA). A random 5 × analyze the true nature of the effect of the dissolved glass
5 mm area was imaged with a 40 µm step for each of the and released ions (Ca , Mg , and others from the glass)
2
2+
2+
three scaffolds at different time points. To quantify the without having any interactions with other salts present
viability results, a maximum intensity projection image in the culture media. It was hypothesized that the effect
was created with red, green, and blue channels using of B3 glass amount on rheological behavior would serve
ImageJ software. The red and green channels of the image as a realistic indicator while using gels made with culture
provided the dead cell and live cell counts. ASC viability media. Despite the evidence in literature demonstrating a
in percentage was calculated using this formula: [live significant difference in the swelling of gels made with DI
cells/(live cells + dead cells)] × 100%. water compared to that of gels made with culture media,
2.10. Statistical analysis the difference is insignificant for viscosity of gels made
Six samples in each set were used for tensile tests, and with DI water or culture media with highly resorbable
36
three samples in each set were used for cell viability B3 glass. It was noticed in our experiments that B3 glass
quantification. The results were reported as average ± dissolves in a few minutes during the gel mixing process to
®
standard deviation. Minitab software was used to analyze significantly affect gel viscosity irrespective of the media
the difference in means of different groups using one-way (DI water or culture media). Figure 3 shows the change
analysis of variance (ANOVA). The means were considered in viscosity of all hydrogels considered in this study with
significantly different if the P-value is less than 0.05. increasing shear rate. The viscosity of alginate (Alg),
Figure 3. Hydrogel viscosity as a function of shear rate at room temperature before crosslinking with CaCl . (a) Alginate, gelatin, and alginate+gelatin (AG)
2
without glass; (b) effect of B3 glass addition on AG hydrogels in different weight concentrations.
Volume 10 Issue 2 (2024) 462 doi. 10.36922/ijb.2057