Page 86 - IJB-6-1
P. 86
Hydrolytic expansion accelerates Fe biodegradation
A B
C D E
F G H
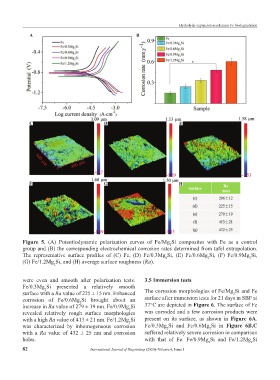
Figure 5. (A) Potentiodynamic polarization curves of Fe/Mg Si composites with Fe as a control
2
group and (B) the corresponding electrochemical corrosion rates determined from tafel extrapolation.
The representative surface profiles of (C) Fe, (D) Fe/0.3Mg Si, (E) Fe/0.6Mg Si, (F) Fe/0.9Mg Si,
2
2
2
(G) Fe/1.2Mg Si, and (H) average surface roughness (Ra).
2
were even and smooth after polarization tests. 3.5 Immersion tests
Fe/0.3Mg Si presented a relatively smooth
2
surface with a Ra value of 225 ± 15 nm. Enhanced The corrosion morphologies of Fe/Mg Si and Fe
2
corrosion of Fe/0.6Mg Si brought about an surface after immersion tests for 21 days in SBF at
2
increase in Ra value of 279 ± 19 nm. Fe/0.9Mg Si 37°C are depicted in Figure 6. The surface of Fe
2
revealed relatively rough surface morphologies was corroded and a few corrosion products were
with a high Ra value of 413 ± 21 nm. Fe/1.2Mg Si present on its surface, as shown in Figure 6A.
2
was characterized by inhomogeneous corrosion Fe/0.3Mg Si and Fe/0.6Mg Si in Figure 6B,C
2
2
with a Ra value of 432 ± 25 nm and corrosion suffered relatively severe corrosion in comparison
holes. with that of Fe. Fe/0.9Mg Si and Fe/1.2Mg Si
2 2
82 International Journal of Bioprinting (2020)–Volume 6, Issue 1