Page 151 - IJB-10-6
P. 151
International Journal of Bioprinting Fluid mechanics of extrusion bioprinting
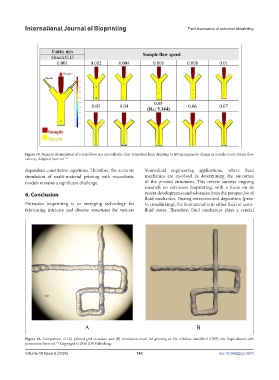
Figure 15. Numerical simulation of coaxial flow in a microfluidic chip. Transition from dripping to jetting regime by change in sample (core) stream flow
velocity. Adapted from ref. 114
Figure 15. Numerical simulation of coaxial flow in a microfluidic chip. Transition from
dependent constitutive equations. Therefore, the accurate biomedical engineering applications, where fluid
dripping to jetting regime by change in sample (core) stream flow velocity. Adapted from ref.
mechanics are involved in determining the outcomes
simulation of multi-material printing with viscoelastic
models remains a significant challenge.
114 of the printed structures. This review surveys ongoing
research on extrusion bioprinting, with a focus on its
6. Conclusion recent developments and advances from the perspective of
fluid mechanics. During extrusion and deposition (prior
Extrusion bioprinting is an emerging technology for to crosslinking), the biomaterial is in either fluid or semi-
fabricating intricate and diverse structures for various fluid states. Therefore, fluid mechanics plays a crucial
A B
Figure 16. Comparison of (A) printed grid structure and (B) simulation result for printing of 4% cellulose nanofibril (CNF) ink. Reproduced with
permission from ref. Copyright © 2018 IOP Publishing.
112
143
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 81 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3973