Page 583 - IJB-10-6
P. 583
International Journal of Bioprinting Biomechanical analysis of mandibular implants
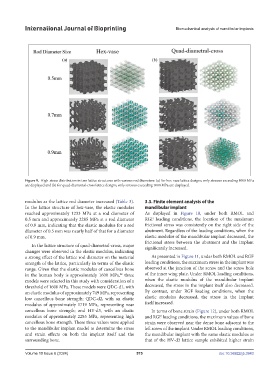
Figure 9. High-stress distribution in two lattice structures with various rod diameters: (a) for hex-vase lattice designs, only stresses exceeding 1000 MPa
are displayed and (b) for quad-diametral-cross lattice designs, only stresses exceeding 1000 MPa are displayed.
modulus as the lattice rod diameter increased (Table 3). 3.3. Finite element analysis of the
In the lattice structure of hex-vase, the elastic modulus mandibular implant
reached approximately 1233 MPa at a rod diameter of As displayed in Figure 10, under both RMOL and
0.5 mm and approximately 2285 MPa at a rod diameter RGF loading conditions, the location of the maximum
of 0.9 mm, indicating that the elastic modulus for a rod frictional stress was consistently on the right side of the
diameter of 0.5 mm was nearly half of that for a diameter abutment. Regardless of the loading conditions, when the
of 0.9 mm. elastic modulus of the mandibular implant decreased, the
frictional stress between the abutment and the implant
In the lattice structure of quad-diametral-cross, major significantly increased.
changes were observed in the elastic modulus, indicating
a strong effect of the lattice rod diameter on the material As presented in Figure 11, under both RMOL and RGF
strength of the lattice, particularly in terms of the elastic loading conditions, the maximum stress in the implant was
range. Given that the elastic modulus of cancellous bone observed at the junction of the screw and the screw hole
in the human body is approximately 1600 MPa, three of the inner wing plate. Under RMOL loading conditions,
22
models were selected in this study with consideration of a when the elastic modulus of the mandibular implant
threshold of 1600 MPa. These models were QDC-d1, with decreased, the stress in the implant itself also decreased.
an elastic modulus of approximately 749 MPa, representing By contrast, under RGF loading conditions, when the
low cancellous bone strength; QDC-d2, with an elastic elastic modulus decreased, the stress in the implant
modulus of approximately 1719 MPa, representing near itself increased.
cancellous bone strength; and HV-d3, with an elastic In terms of bone strain (Figure 12), under both RMOL
modulus of approximately 2285 MPa, representing high and RGF loading conditions, the maximum values of bone
cancellous bone strength. These three values were applied strain were observed near the dense bone adjacent to the
to the mandibular implant model to determine the stress left screw of the implant. Under RMOL loading conditions,
and strain effects on both the implant itself and the the mandibular implant with the same elastic modulus as
surrounding bone. that of the HV-d3 lattice sample exhibited higher strain
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 575 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3943