Page 585 - IJB-10-6
P. 585
International Journal of Bioprinting Biomechanical analysis of mandibular implants
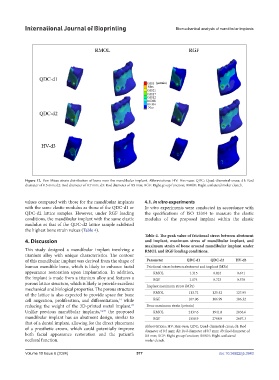
Figure 12. Von Mises strain distribution of bone near the mandibular implant. Abbreviations: HV: Hex-vase; QDC: Quad-diametral-cross; d1: Rod
diameter of 0.5 mm; d2: Rod diameter of 0.7 mm; d3: Rod diameter of 0.9 mm; RGF: Right group function; RMOL: Right unilateral molar clench.
values compared with those for the mandibular implants 4.1. In vitro experiments
with the same elastic modulus as those of the QDC-d1 or In vitro experiments were conducted in accordance with
QDC-d2 lattice samples. However, under RGF loading the specifications of ISO 13314 to measure the elastic
conditions, the mandibular implant with the same elastic modulus of the proposed implant within the elastic
modulus as that of the QDC-d2 lattice sample exhibited
the highest bone strain values (Table 4).
Table 4. The peak value of frictional stress between abutment
4. Discussion and implant, maximum stress of mandibular implant, and
maximum strain of bone around mandibular implant under
This study designed a mandibular implant involving a RMOL and RGF loading conditions.
titanium alloy with unique characteristics. The contour
of this mandibular implant was derived from the shape of Parameter QDC-d1 QDC-d2 HV-d3
human mandible bone, which is likely to enhance facial Frictional stress between abutment and implant (MPa)
appearance restoration upon implantation. In addition, RMOL 1.315 0.824 0.671
the implant is made from a titanium alloy and features a RGF 1.074 0.723 0.578
porous lattice structure, which is likely to provide excellent Implant maximum stress (MPa)
mechanical and biological properties. The porous structure
of the lattice is also expected to provide space for bone RMOL 113.72 125.42 127.95
cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation, while RGF 107.06 106.99 106.32
14
reducing the weight of the 3D-printed metal implant. Bone maximum strain (µstrain)
27
Unlike previous mandibular implants, 14,28 the proposed RMOL 2137.6 1941.8 2836.6
mandibular implant has an abutment design, similar to RGF 1558.9 2708.9 2697.3
that of a dental implant, allowing for the direct placement
of a prosthetic crown, which could potentially improve Abbreviations: HV: Hex-vase; QDC: Quad-diametral-cross; d1: Rod
diameter of 0.5 mm; d2: Rod diameter of 0.7 mm; d3: Rod diameter of
both facial appearance restoration and the patient’s 0.9 mm; RGF: Right group function; RMOL: Right unilateral
occlusal function. molar clench.
Volume 10 Issue 6 (2024) 577 doi: 10.36922/ijb.3943