Page 109 - IJB-8-2
P. 109
Lee, et al.
, and quadra-shaped EADs. This tendency can possibly case. Consequently, the average values of H max were
be attributed to the difference in the internal area, where measured to be 394, 220.6, 223.2, and 228.8 mm for the
urine can flow during the reflex. When the internal areas DJ stent without EAD and with single, double, and triple
of each EAD were measured using the CAD model, the penta-shaped EADs, respectively, as shown in Figure 7D.
penta-, quadra-, octa-, and hexa-shaped EADs showed The results showed that no significant variations existed
areas of 46.53, 46.01, 45.94, and 44.94 mm , respectively. in H max between the single, double, and triple EADs. This
2
As the internal area increased, the EAD has the potential might be because the pressure gradient, which helps the
to be expanded because more urine flow can be trapped EAD expand, was significantly decreased across the EAD
inside the EAD when initial reflux occurs. In addition, the at Position #1. Due to the decreased pressure gradient,
external area (i.e., the spatial area between the expanded the subsequent EADs (i.e., EADs at Positions #2 and #3)
EAD wall and the inner wall of the ureter) will decrease did not fully expand to sufficiently block the ureter line.
as the internal area of EAD increases, thus increasing the Thus, water flowed in the external area, and the EADs
flow resistance in the ureter, which results in reduced H max . at Positions #2 or #3 may not work. This also indicated
Although the internal area of the quadra-shaped EAD that a single EAD attached at Position #1 (near the VUJ)
is larger than that of the hexa- and octa-shaped EADs, sufficed to mitigate urine reflux in the ureter line. From
its anti-reflux efficiency is lower than that of the others. the results shown in Figures 6 and 7, a single penta-
Here, the quadra-shaped EAD was flipped (overturned) shaped EAD at Position #1 had the best performance in
during the reflux because the number of ribs was not preventing reflux, and the anti-reflux performance did
enough to maintain the overall shape against reflex not change significantly depending on the number of
pressure. Therefore, the quadra-shaped EAD showed the attached EADs. In summary, the device with the highest
worst anti-reflux efficiency in this study. effectiveness and least irritation to patients was found to
To further characterize the anti-reflux effectiveness be a single penta-shaped EAD at Position #1 in this study.
with respect to the number of attached EADs, an Table 1 shows a comparison of anti-reflex devices
experiment was performed using an increasing number between this study and previous literature to reduce
of penta-shaped EADs, which exhibited the best the VUR. It was noteworthy that previous studies
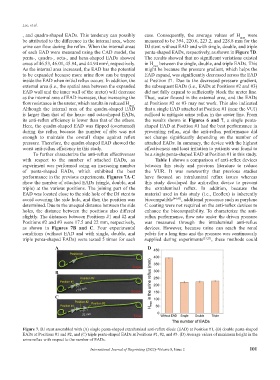
performance in the previous experiments. Figures 7A-C have focused on intraluminal reflux issues whereas
show the number of attached EADs (single, double, and this study developed the anti-reflux device to prevent
triple) at the various positions. The joining part of the the extraluminal reflux. In addition, because the
EAD was located close to the side hole of the DJ stent to material used in this study (i.e., Ecoflex) is inherently
avoid covering the side hole, and then the position was biocompatible [44,45] , additional processes such as parylene
determined. Due to the unequal distance between the side C coating were not required on the anti-reflex devices to
holes, the distance between the positions also differed enhance the biocompatibility. To characterize the anti-
slightly. The distances between Positions #1 and #2 and reflux performance, flow rate under the driven pressure
Positions #2 and #3 were 17.5 and 22 mm, respectively, was measured through the intraluminal anti-reflux
as shown in Figures 7B and C. Four experimental devices. However, because urine can reach the renal
conditions (without EAD and with single, double, and pelvis for a long time and the pressure was continuously
triple penta-shaped EADs) were tested 5 times for each supplied during experiments [21,23] , these methods could
A D
D
B
C
Figure 7. DJ stent assembled with (A) single penta-shaped extraluminal anti-reflux diode (EAD) at Position #1, (B) double penta-shaped
EADs at Positions #1 and #2, and (C) triple penta-shaped EADs at Positions #1, #2, and #3. (D) Average values of maximum height in the
urine reflux with respect to the number of EADs.
International Journal of Bioprinting (2022)–Volume 8, Issue 2 101