Page 214 - IJB-9-1
P. 214
International Journal of Bioprinting FeS /PCL scaffold for bone regeneration
2
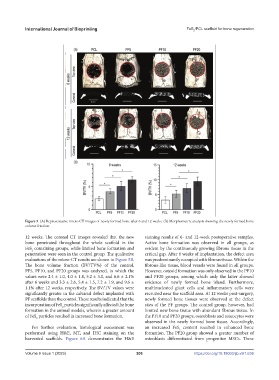
Figure 5. (A) Representative micro-CT images of newly formed bone after 6 and 12 weeks. (B) Morphometric analysis showing the newly formed bone
volume fraction.
12 weeks. The coronal CT images revealed that the new staining results of 6- and 12-week postoperative samples.
bone penetrated throughout the whole scaffold in the Active bone formation was observed in all groups, as
FeS containing groups, while limited bone formation and evident by the continuously growing fibrous tissue in the
2
penetration were seen in the control group. The qualitative critical gap. After 6 weeks of implantation, the defect area
evaluations of the micro-CT results are shown in Figure 5B. was predominantly occupied with fibrous tissue. Within the
The bone volume fraction (BV/TV%) of the control, fibrous-like tissue, blood vessels were found in all groups.
PF5, PF10, and PF20 groups was analyzed, in which the However, osteoid formation was only observed in the PF10
values were 2.4 ± 1.0, 4.0 ± 1.8, 5.2 ± 3.0, and 6.6 ± 2.1% and PF20 groups, among which only the latter showed
after 6 weeks and 3.3 ± 2.6, 5.4 ± 1.5, 7.2 ± 1.9, and 9.6 ± evidence of newly formed bone island. Furthermore,
1.1% after 12 weeks, respectively. The BV/TV values were multinucleated giant cells and inflammatory cells were
significantly greater in the calvarial defect implanted with recruited near the scaffold area. At 12 weeks post-surgery,
PF scaffolds than the control. These results indicated that the newly formed bone tissues were observed at the defect
incorporation of FeS particles significantly affected the bone sites of the PF groups. The control group, however, had
2
formation in the animal models, wherein a greater amount limited new bone tissue with abundant fibrous tissue. In
of FeS particles resulted in increased bone formation. the PF10 and PF20 groups, osteoblasts and osteocytes were
2
observed in the newly formed bone tissue. Accordingly,
For further evaluation, histological assessment was an increased FeS content resulted in enhanced bone
2
performed using H&E, MT, and IHC staining on the formation. The PF20 group showed a greater number of
harvested scaffolds. Figure 6A demonstrates the H&E osteoblasts differentiated from progenitor MSCs. These
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023)olume 9 Issue 1 (2023)
V 206 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.636