Page 75 - IJB-9-1
P. 75
International Journal of Bioprinting Osteoconduction and scaffold directionality
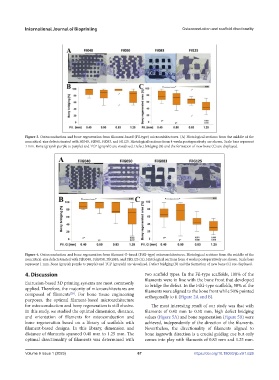
Figure 3. Osteoconduction and bone regeneration from filament-based (Fil-type) microarchitectures. (A) Histological sections from the middle of the
noncritical-size defects treated with Fil040, Fil050, Fil083, and Fil125. Histological sections from 4 weeks postoperatively are shown. Scale bars represent
1 mm. Bone (grayish purple to purple) and TCP (grayish) are visualized. Defect bridging (B) and the formation of new bone (C) are displayed.
Figure 4. Osteoconduction and bone regeneration from filament G-based (FilG-type) microarchitectures. Histological sections from the middle of the
noncritical-size defects treated with FilG040, FilG050, FilG083, and FilG125 (A). Histological sections from 4 weeks postoperatively are shown. Scale bars
represent 1 mm. Bone (grayish purple to purple) and TCP (grayish) are visualized. Defect bridging (B) and the formation of new bone (C) are displayed.
4. Discussion two scaffold types. In the Fil-type scaffolds, 100% of the
filaments were in line with the bone front that developed
Extrusion-based 3D printing systems are most commonly to bridge the defect. In the FilG-type scaffolds, 50% of the
applied. Therefore, the majority of microarchitectures are filaments were aligned to the bone front while 50% pointed
composed of filaments . For bone tissue engineering orthogonally to it (Figure 2A and B).
[29]
purposes, the optimal filament-based microarchitecture
for osteoconduction and bony regeneration is still elusive. The most interesting result of our study was that with
In this study, we studied the optimal dimension, distance, filaments of 0.40 mm to 0.50 mm, high defect bridging
and orientation of filaments for osteoconduction and values (Figure 5A) and bone regeneration (Figure 5B) were
bone regeneration based on a library of scaffolds with achieved, independently of the direction of the filaments.
filament-based designs. In this library, dimension and Nevertheless, the directionality of filaments aligned to
distance of filaments spanned 0.40 mm to 1.25 mm. The bone ingrowth direction is a crucial guiding cue but only
optimal directionality of filaments was determined with comes into play with filaments of 0.83 mm and 1.25 mm.
Volume 9 Issue 1 (2023)olume 9 Issue 1 (2023) 67 https://doi.org/10.18063/ijb.v9i1.626
V